Transcription factors in Orinus: novel insights into transcription regulation for speciation adaptation on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau
- PMID: 40301765
- PMCID: PMC12042605
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06602-x
Transcription factors in Orinus: novel insights into transcription regulation for speciation adaptation on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau
Abstract
Background: Transcription factors (TFs) are crucial regulators of plant growth, development, and resistance to environmental stresses. However, comprehensive understanding of the roles of TFs in speciation of Orinus, an extreme-habitat plant on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, is limited.
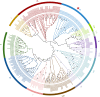
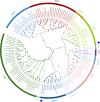
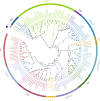
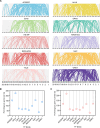
Results: Here, we identified 52 TF families, including 2125 members in Orinus, by methodically analysing domain findings, gene structures, chromosome locations, conserved motifs, and phylogenetic relationships. Phylogenetic trees were produced for each Orinus TF family using protein sequences together with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) TFs to indicate the subgroups. The differences between Orinus and wheat species in terms of TF family size implies that both Orinus- and wheat-specific subfamily contractions (and expansions) contributed to the high adaptability of Orinus. Based on deep mining of RNA-Seq data between two species of Orinus, O. thoroldii and O. kokonoricus, we obtained differentially expressed TFs (DETFs) in 20 families, most of which were expressed higher in O. thoroldii than in O. kokonoricus. In addition, Cis-element analysis shows that MYC and G-box elements are enriched in the promoter region of DETFs, suggesting that jasmonic acid (JA) and abscisic acid (ABA) act synergistically in Orinus to enhance the signalling of related abiotic stress responses, ultimately leading to an improvement in the stress tolerance and speciation adaptation of Orinus.
Conclusions: Our data serve as a genetic resource for Orinus, not only filling the gap in studies of TF families within this genus but also providing preliminary insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying speciation in Orinus.
Keywords: Orinus; Phylogenetic relationship; Speciation adaptation; Transcription factor; Transcriptional regulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors approved the final manuscript and the submission to this journal. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Program No. 2023-ZJ-706/the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 32360305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

