Dual-specific phosphatases-8: a new target for clinical disease intervention
- PMID: 40301852
- PMCID: PMC12042392
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06499-y
Dual-specific phosphatases-8: a new target for clinical disease intervention
Abstract
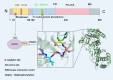
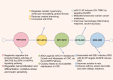
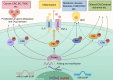
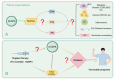
Dual-specific phosphatase-8 (DUSP8), identified as the first gene in a genome-wide association study (GWAS), is implicated in cellular oxidative stress, proliferation, apoptosis, and drug resistance through its negative regulation of the dephosphorylation activities of JNK, ERK, and p38 within the MAPK pathway. Recent studies have shown that DUSP8 plays a pivotal role in the progression of several human diseases, notably colorectal cancer, diabetic kidney disease, and breast cancer. This suggests that DUSP8 may represent a novel target for clinical intervention in these diseases. This review first introduces the biological structure and function of DUSP8, with a focus on its relationship with a series of diseases and the regulatory mechanisms involved. Furthermore, we concentrate on unresolved scientific questions in the current research, aiming to establish a new theoretical foundation for the diagnosis and treatment of related diseases.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; DUSP8; Diabetic kidney disease; MAPK; Regulatory mechanism.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that we have no relevant financial or non-financial interests that could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest in relation to the research and writing of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Mustelin T. A brief introduction to the protein phosphatase families. Methods in molecular biology. (Clifton N J). 2007;365:9–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

