Development and validation of machine learning models for predicting no. 253 lymph node metastasis in left-sided colorectal cancer using clinical and CT-based radiomic features
- PMID: 40301906
- PMCID: PMC12039209
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-025-00876-y
Development and validation of machine learning models for predicting no. 253 lymph node metastasis in left-sided colorectal cancer using clinical and CT-based radiomic features
Abstract
Background: The appropriate ligation level of the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) in left-sided colorectal cancer (CRC) surgery is debated, with metastasis in No. 253 lymph node (No. 253 LN) being a key determining factor. This study aimed to develop a machine learning model for predicting metastasis in No. 253 LN.
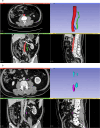
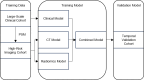
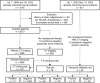
Methods: We retrospectively collected clinical data from 2,118 patients with left-sided CRC and contrast-enhanced CT images from 310 of these patients. From this data, a test set, a training set, and a temporal validation set were constructed. Logistic regression models were used to develop a clinical model, a CT model, and a radiomics model, which were then integrated into a combined model using logical rules. Finally, these models were evaluated using metrics such as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), precision-recall (PR) curves, decision curve analysis (DCA), net reclassification improvement (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
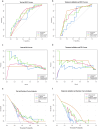
Results: A clinical model, a CT model, and a radiomics model were constructed using univariate logistic regression. A combined model was developed by integrating the clinical, CT, and radiomics models, with positivity defined as all three models being positive at a 90% sensitivity threshold. The clinical model included six predictive factors: tumor site, endoscopic obstruction, CEA levels, growth type, differentiation grade, and pathological classification. The CT model utilized largest lymph node average CT value, short-axis diameter and long-axis diameter. The radiomics model incorporated maximum gray level intensity within the region of interest, large area high gray level emphasis, small area high gray level emphasis and surface area to volume ratio. In the test set, the AUCs for the clinical, CT, radiomics, and combined models were 0.694, 0.663, 0.72, and 0.663, respectively, while in the temporal validation set, they were 0.743, 0.629, 0.716, and 0.8. Specifically, the combined model demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.8 and a specificity of 0.8 in the temporal validation set. By comparing the PR and DCA curves, the combined model demonstrated better performance. Additionally, the combined model showed moderate improvements in INR and IDI compared to other models.
Conclusion: A clinical and CT-based radiomics model shows promise in predicting No. 253 LN metastasis in left-sided CRC and provides insights for optimizing IMA ligation strategies.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Lymph node metastasis; Machine learning; Prediction model; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This retrospective study was approved by Ethics Committee of Peking University First Hospital, waiving the need for written informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2-[18F]FDG PET-based quantification of lymph node metabolic heterogeneity for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 May;51(6):1729-1740. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06578-6. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38150017
-
Prediction of peripheral lymph node metastasis (LNM) in thyroid cancer using delta radiomics derived from enhanced CT combined with multiple machine learning algorithms.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Mar 13;30(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02438-1. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40075509 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of lateral lymph node metastasis with short diameter less than 8 mm in papillary thyroid carcinoma based on radiomics.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Nov 15;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00803-7. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39548590 Free PMC article.
-
The Application Status of Radiomics-Based Machine Learning in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 5;27:e69906. doi: 10.2196/69906. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40323647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning and deep learning models for preoperative detection of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 May;50(5):1927-1941. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04668-z. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39522103
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Tryliskyy Y, Wong CS, Demykhova I, Tyselskyi V, Kebkalo A, Poylin V. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials evaluating the effect of the level of ligation of inferior mesenteric artery on functional outcomes in rectal cancer surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2022;37(3):709–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82274015/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82372860/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JQ24059/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation
- 2021CR03/Youth Clinical Research Project of Peking University First Hospital
- BMU2020PYB026/Youth Cultivated Research Fund of Peking University Health Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

