Repurposing of epalrestat for neuroprotection in parkinson's disease via activation of the KEAP1/Nrf2 pathway
- PMID: 40301912
- PMCID: PMC12042445
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03455-x
Repurposing of epalrestat for neuroprotection in parkinson's disease via activation of the KEAP1/Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
Background: Epalrestat (EPS), an aldose reductase inhibitor, is used to alleviate peripheral nerve disorder of diabetic patients in clinical therapy. Even though EPS exerted effects in central nervous system diseases, the neuroprotection and underlying molecular mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases, especially Parkinson's disease (PD), remains obscure. Our study aimed to investigate the potential of EPS suppressed PD progression both in vivo and in vitro.
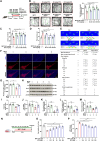
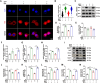
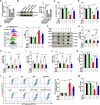
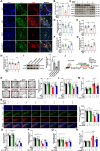
Methods: We used 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridillium ion (MPP+)-treated PD cells and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated PD mice to investigate the protective function and molecular mechanism of EPS in PD. EPS was administered three times daily through oral route 3 days before model establishment for 5 consecutive days. Behavioral manifestation of mice was conducted using open field test, rotarod test and CatWalk gait analysis. Immunofluorescence was used to detect dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons survival in the substantia nigra. Subsequently, oxidative stress, mitochondrial function and KEAP1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in PD models were detected through molecular biology methods to assess the effect and downstream mechanisms of EPS on PD. Molecular docking, surface plasmon resonance and cellular thermal shift assay were used to verify the direct binding of EPS and KEAP1.
Results: We found that EPS exhibited potent antiparkinsonian activity in PD models both in vivo and in vitro. PD models treated with EPS manifested alleviated oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Furthermore, we found EPS activated the Nrf2 signaling pathway which contributed to DAergic neurons survival in PD models. Particularly, we firstly confirmed that EPS competitively binds to KEAP1 and enhanced its degradation, thereby activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Collectively, EPS attenuates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction by directly binding KEAP1 to activate the KEAP1/Nrf2 signaling pathway, further reducing DAergic neurons damage. These findings suggest that EPS has great potential to become a therapeutic for PD as a clinically effective and safe medicine.
Keywords: Epalrestat; KEAP1; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Nrf2; Oxidative stress; Parkinson’s disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were performed following international guidelines and conducted in accordance with the Animal Ethics Committee of Qingdao University (QDU-AEC-2024766). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The principal molecular mechanisms behind the activation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway leading to neuroprotective action in Parkinson's disease.Neurochem Int. 2022 Jun;156:105325. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105325. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Neurochem Int. 2022. PMID: 35278519 Review.
-
Distinct Nrf2 Signaling Mechanisms of Fumaric Acid Esters and Their Role in Neuroprotection against 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Experimental Parkinson's-Like Disease.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 8;36(23):6332-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0426-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27277809 Free PMC article.
-
Tetramethylpyrazine nitrone exerts neuroprotection via activation of PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway in Parkinson's disease models.J Adv Res. 2024 Oct;64:195-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.021. Epub 2023 Nov 19. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37989471 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel ethyl ferulate derivatives as potent Keap1 inhibitors to activate the Nrf2/ARE pathway in Parkinson's disease.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;494:117172. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2024.117172. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39603427
-
Unraveling neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease: Nrf2-Keap1 pathway's vital role amidst pathogenic pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):2801-2820. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01549-1. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39136812 Review.
References
-
- Choudhary S, Silakari O. Virtual screening of epalrestat mimicking selective ALR2 inhibitors from natural product database: auto pharmacophore, ADMET prediction and molecular dynamics approach. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:6052–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

