The impact of preoperative immunonutritional status on postoperative complications in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 40301987
- PMCID: PMC12038932
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-025-01624-3
The impact of preoperative immunonutritional status on postoperative complications in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Preoperative immunonutritional status can influence postoperative complications. Malnutrition in ovarian cancer patients diminishes the body's resilience to abdominal surgery, resulting in inferior surgical outcomes and increased postoperative complications. We aim to investigate the effect of preoperative immunonutritional status, including NLR, PLR, LMR, TCLR, FAR, FLR, SII, PNI and CONUT on postoperative complications in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) in a large population.
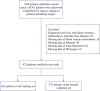
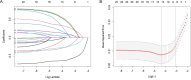
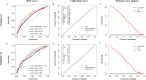
Methods: A multicenter real-world study included 922 patients with histologically confirmed EOC who received comprehensive staged surgery or debulking surgery at seven tertiary hospitals in China between 2012 and 2023. Logistic regression and Lasso regression analyses were employed to identify variables associated with postoperative complications. A predictive nomogram model was developed based on multivariate modeling.
Results: The study included a total of 922 patients diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer across seven medical centers with 565 (61.3%) patients experiencing postoperative complications. Significant differences were found in the distribution of inflammatory and nutritional risk indicators, including NLR, PLR, LMR, TCLR, FAR, FLR, SII, PNI and CONUT between the two groups (all P < 0.01). A multivariable model identified several predictive factors for postoperative complications: PNI > 46.73 (odds ratio [OR] = 0.49, P < 0.001), FAR > 10.77 (OR = 1.60, P = 0.019), LMR > 3.70 (OR = 0.68, P = 0.044), hydrothorax (OR = 2.60, P = 0.005), laparoscopy (OR = 0.59, P = 0.010 vs. laparotomy), enterectomy (OR = 2.50, P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Poor immunonutritional status can increase the risk of postoperative complications. These findings suggest that prompt nutritional interventions may reduce the incidence of postoperative complications and improve surgical outcomes. The risk prediction model, including PNI, FAR, LMR, hydrothorax, laparoscopy vs. laparotomy, and enterectomy, might facilitate patient-centered decision-making and risk stratification.
Clinical trial registration: The study was registered in the Clinical trial registry: NCT06483399. ( https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06483399 ).
Keywords: Ovarian cancer; Postoperative complications; Preoperative immunonutritional status.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Commission of Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (TJ-IRB202401053) and the consent was waived. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. 10.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- du Bois A, Reuss A, Pujade-Lauraine E, Harter P, Ray-Coquard I, Pfisterer J. Role of surgical outcome as prognostic factor in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer: a combined exploratory analysis of 3 prospectively randomized phase 3 multicenter trials: by the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynaekologische Onkologie Studiengruppe Ovarialkarzinom (AGO-OVAR) and the Groupe d’Investigateurs Nationaux Pour Les Etudes des Cancers de l’Ovaire (GINECO). Cancer. 2009;115:1234–44. 10.1002/cncr.24149. - PubMed
-
- Manning-Geist BL, Hicks-Courant K, Gockley AA, Clark RM, Del Carmen MG, Growdon WB, Horowitz NS, Berkowitz RS, Muto MG, Worley MJ. Jr. A novel classification of residual disease after interval debulking surgery for advanced-stage ovarian cancer to better distinguish oncologic outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:326e1. 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.05.006. - PubMed
-
- Chang SJ, Hodeib M, Chang J, Bristow RE. Survival impact of complete cytoreduction to no gross residual disease for advanced-stage ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130:493–8. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.05.040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772787, 82072889/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- 20A0769/Major Project of Chinese Society of Medical Education
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2019AZZD-0359, Y-2019AZQN-0385/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

