Neuronal α-Synuclein Disease Stage Progression over 5 Years
- PMID: 40302527
- PMCID: PMC12273616
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.30191
Neuronal α-Synuclein Disease Stage Progression over 5 Years
Abstract
Background: Neuronal α-synuclein disease (NSD) is defined by the presence of an in vivo biomarker of neuronal alpha-synuclein (n-asyn) pathology. The NSD integrated staging system (NSD-ISS) for research describes progression across the disease continuum as stages 0 to 6.
Objective: The aim was to assess 5-year longitudinal change in NSD-ISS in early disease.
Methods: Analysis included a subset of participants from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) enrolled before 2020 as Parkinson's disease (PD) patients, prodromal PD patients, or healthy controls (HC) who met NSD criteria. Staging was defined based on biomarkers of n-asyn and dopaminergic dysfunction in early stages, clinical features, and severity of functional impairment in stages 3 to 6. Stages were determined annually for 5 years.
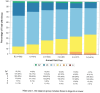
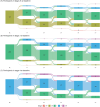
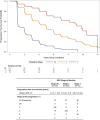
Results: Of 576 NSD participants, 494 were enrolled as PD patients, 74 prodromal PD patients, and 8 HCs. At baseline, 24% of participants were stage 2B, 56% Stage 3, 13% stage 4, and less than 5% in other stages. At year 5, the respective percentages for stages 2B to 4 were 11%, 50%, and 34%, indicating progression through NSD stages. Progression was driven by functional impairment in the predominantly motor domain (95%) for stage 2B to 3, increasing degree of nonmotor dysfunction for stages 3 to 4 (46%), and a combination of domains for stages 4 to 5. Initiation of dopaminergic medications led to stage regression in 8% of participants in Stage 3 but 41% in stage 4.
Conclusions: Our analysis supports the utility of NSD-ISS in defining the stages of disease progression, at least in the early clinical and prodromal stages (2B, 3, or 4), suggesting the value of NSD-ISS as a potential research tool for drug development. Further research involving preclinical cohorts is a crucial next step. © 2025 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; biological definition; dementia with Lewy bodies; neuronal α‐synuclein disease.
© 2025 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
References
-
- Simuni T, Chahine LM, Poston K, et al. A biological definition of neuronal alpha‐synuclein disease: towards an integrated staging system for research. Lancet Neurol 2024;23:178–190. - PubMed
-
- Hoglinger GU, Adler CH, Berg D, et al. A biological classification of Parkinson's disease: the SynNeurGe research diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 2024;23:191–204. - PubMed
-
- Pagano G, Taylor KI, Anzures‐Cabrera J, et al. Trial of Prasinezumab in early‐stage Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 2022;387:421–432. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

