Nano-strategies for Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 40302816
- PMCID: PMC12036086
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.108194
Nano-strategies for Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
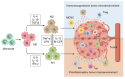
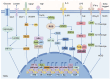
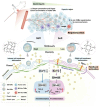
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are one type of the most abundant immune cells within tumor, resulting in immunosuppresive tumor microenvironment and tumor resistance to immunotherapy. Thus, targeting TAMs is a promising therapeutic strategy for boosting cancer immunotherapy. This study provides an overview of current therapeutic strategies targeting TAMs, which focus on blocking the recruitment of TAMs by tumors, regulating the polarization of TAMs, and directly eliminating TAMs using various nanodrugs, especially with a new categorization based on the specific signaling pathways, such as NF-κB, HIF-1α, ROS, STAT, JNK, PI3K, and Notch involved in their regulatory mechanism. The latest developments of nanodrugs modulating these pathways are discussed in determining the polarization of TAMs and their role in the tumor microenvironment. Despite the challenges in clinical translation and the complexity of nanodrug synthesis, the potential of nanodrugs in enhancing the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy is worthy of expecting.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; M1 polarization; Nanodrugs; Signaling pathways; Tumor-associated macrophages.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Zemek RM, Anagnostou V, Pires da Silva I, Long GV, Lesterhuis WJ. Exploiting temporal aspects of cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024;24:480–97. - PubMed
-
- Yang K, Halima A, Chan TA. Antigen presentation in cancer - mechanisms and clinical implications for immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:604–23. - PubMed
-
- Nasir I, McGuinness C, Poh AR, Ernst M, Darcy PK, Britt KL. Tumor macrophage functional heterogeneity can inform the development of novel cancer therapies. Trends Immunol. 2023;44:971–85. - PubMed
-
- Gunassekaran GR, Poongkavithai Vadevoo SM, Baek M-C, Lee B. M1 macrophage exosomes engineered to foster M1 polarization and target the IL-4 receptor inhibit tumor growth by reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages into M1-like macrophages. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121137. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

