Genetic and Pathogenic Characteristics of an Emerging Highly Virulent Recombinant Lineage Korean Clade C PRRSV Strain
- PMID: 40303075
- PMCID: PMC12016962
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/5785557
Genetic and Pathogenic Characteristics of an Emerging Highly Virulent Recombinant Lineage Korean Clade C PRRSV Strain
Abstract
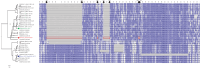
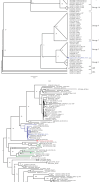
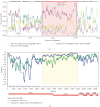
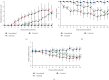
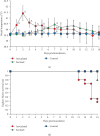
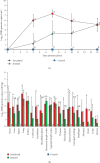
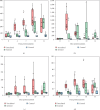
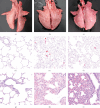
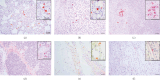
A strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) was isolated from lung tissue of a pig showing severe respiratory clinical signs from a farm in Gyeongsang province of South Korea. This PRRSV strain, designated as SNUVR220803, was classified within the lineage Korean clade C (LKC) based on a phylogenetic analysis of the ORF5 gene. A whole-genome analysis was conducted on the SNUVR220803 strain, which appears to be a recombinant between the PRRSV strains K07-2273 (part of LKC lineage) and Ingelvac MLV (part of Lineage 5). The Nsp2 amino acid sequence of this strain features a deletion of four additional amino acids, setting it apart from the typical Korean clades A, B, and C lineages. An animal inoculation experiment was conducted with 24 pigs divided into three groups: 12 pigs in the inoculated group, six in the sentinel group, and six in the negative control group. Inoculated pigs exhibited persisting hyperthermia (≥40.3°C) for 5 days, palpebral edema, and cyanosis. Subsequently, these pigs suffered from severe respiratory distress and cachexia, leading to a mortality rate of 58.3% (7 out of 12 pigs) at 14 days postinoculation (dpi). Body weight decreased post-SNUVR220803 strain infection in both the inoculated and sentinel groups. Gross pathology revealed noncollapsed lungs and serous effusion in the pericardial and peritoneal cavities. Microscopic analysis revealed severe interstitial pneumonia, while immunohistochemistry confirmed the presence of PRRSV antigen in the lungs, lymph nodes, thymus, kidneys, and the heart. Additionally, the levels of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-α (IFN-α), and IL-10 were significantly elevated in the plasma of infected pigs. These observations indicate that the LKC recombinant strain, combined with Lineage 5, possesses high virulence and infectivity as characterized by distinctive exudative lesions.
Copyright © 2024 Jeongmin Suh and Chanhee Chae.
Conflict of interest statement
The author received support for the research presented in this article. However, this support did not exert any influence on the scientific content or stance of the research presented in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cavanagh D. Nidovirales: a new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Archives of Virology . 1997;142(3):629–633. - PubMed
-
- Kang H., Yu J. E., Shin J.-E., et al. Geographic distribution and molecular analysis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses circulating in swine farms in the Republic of Korea between 2013 and 2016. BMC Veterinary Research . 2018;14(1) doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1480-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

