Comparative Analysis of Proteinuria and Longitudinal Outcomes in Immune Complex Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis and C3 Glomerulopathy
- PMID: 40303231
- PMCID: PMC12034854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.01.024
Comparative Analysis of Proteinuria and Longitudinal Outcomes in Immune Complex Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis and C3 Glomerulopathy
Abstract
Introduction: C3 glomerulopathy (C3G) and primary immune complex-mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (IC-MPGN) are rare diseases that share a similar pathogenesis; however, the prognostic significance of proteinuria reduction remains poorly characterized. This study compared the outcomes in C3G and IC-MPGN and assessed the impact of changes in proteinuria on kidney prognosis.
Methods: This retrospective, longitudinal, multicenter study used joint linear mixed-effects models to assess proteinuria trajectories, and Cox regression to evaluate their association with kidney failure. In addition, time-averaged proteinuria (TA-P) was calculated to determine its impact on kidney prognosis.
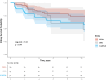
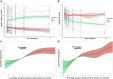
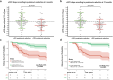
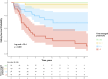
Results: The study included 149 patients: 98 with C3G (66%) and 51 with IC-MPGN (34%) with a median age of 35 (interquartile range [IQR]: 22-53) years. During a median follow-up of 65 (IQR: 32-114) months, 44 patients (30%) progressed to kidney failure without differences across C3G or IC-MPGN. A strong association was observed between longitudinal increase in proteinuria and the risk of kidney failure. In addition, a ≥ 50% proteinuria reduction over time was associated with a lower risk of kidney failure (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.61; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.46-0.75, P < 0.001). Results were consistent in both C3G and IC-MPGN, and in those with baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥ 30 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and proteinuria ≥ 1 g/d. A ≥30% proteinuria reduction at 6 months or a ≥50% proteinuria reduction at 12 months were associated with a slower eGFR decline. Patients were categorized into 4 subgroups based on TA-P levels, with TA-P values < 1 g/d indicating better kidney outcomes.
Conclusion: Proteinuria reduction was associated with improved kidney outcomes and slower eGFR decline in both C3G and IC-MPGN.
Keywords: C3 glomerulopathy; glomerular filtration rate; kidney failure; membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; proteinuria.
© 2025 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

