Early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Promotes Recovery of Blunt Liver Injury in Rats via Inhibiting Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 40303491
- PMCID: PMC12035843
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.109842
Early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Promotes Recovery of Blunt Liver Injury in Rats via Inhibiting Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
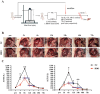
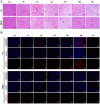
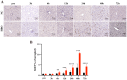
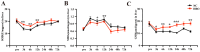
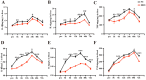
Purpose: Blunt Liver Injury (BLI) is a common form of blunt abdominal trauma, with most cases managed non-surgically in current clinical practice. However, the absence of targeted treatments addressing the pathological changes associated with liver injury can result in prolonged recovery and potential long-term complications. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, has shown therapeutic potential in various diseases. This prospective randomized controlled experimental animal trial aimed to evaluate the effect of HBOT on BLI in a rat model. Methods: We established a BLI rat model by employing a free-fall weight method. Following injury, one group received no intervention, while the other was treated with HBOT (2.5 ATA, 60 minutes per session, once daily). Liver tissue and serum samples were collected at multiple time points for histological evaluation (HE staining), apoptosis detection (TUNEL staining), proliferation assessment (Ki67 immunohistochemical staining), and measurements of liver transaminase (ALT, AST), inflammatory markers (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), and oxidative stress indicators (SOD, MDA, GSH). Results: The results indicated that HBOT significantly reduced liver transaminase elevation, pathological damage, and hepatocyte apoptosis while promoting hepatocyte proliferation and accelerating liver function recovery. Mechanistically, HBOT alleviated oxidative stress and inflammatory response, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Conclusion: These findings provide further evidence supporting the application of HBOT in the clinical management of BLI. This study helps advance the clinical approach to BLI by shifting the focus from symptom management to mechanism-based treatment.
Keywords: blunt liver injury; hyperbaric oxygen therapy; inflammatory response; oxidative stress.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quercetin in combination with hyperbaric oxygen therapy synergistically attenuates damage progression in traumatic spinal cord injury in a rat model.J Chem Neuroanat. 2023 Mar;128:102231. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2023.102231. Epub 2023 Jan 7. J Chem Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36627061
-
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment reverses radiation induced pro-fibrotic and oxidative stress responses in a rat model.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Feb;103:248-255. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.12.036. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28034833
-
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and N-acetylcysteine ameliorate acetaminophen-induced liver injury in a rat model.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013 Oct;32(10):1107-16. doi: 10.1177/0960327113499167. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23925941
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment: Effects on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 3;11(12):1827. doi: 10.3390/biom11121827. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Emerging Evidence and Clinical Applications of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.J Intensive Care Med. 2025 Mar;40(3):341-351. doi: 10.1177/08850666241313136. Epub 2025 Jan 15. J Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 39814353 Review.
References
-
- Chen T, Shuang R, Gao T, Ai L, Diao J, Yuan X. et al. OPA1 Mediated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Hepatocyte: The Novel Insight for Melatonin Attenuated Apoptosis in Concanavalin A Induced Acute Liver Injury. J Pineal Res. 2024;76:e70010. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

