Synergistic efficiency of modified banana leaf derived cellulose-g-C3N4 hybrid composite: a sustainable approach for visible-light-driven photodegradation of dyes
- PMID: 40303559
- PMCID: PMC12038391
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra01156f
Synergistic efficiency of modified banana leaf derived cellulose-g-C3N4 hybrid composite: a sustainable approach for visible-light-driven photodegradation of dyes
Abstract
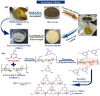
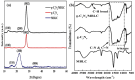
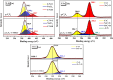
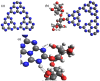
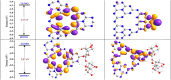
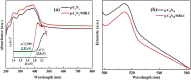
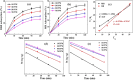
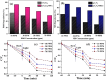
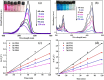
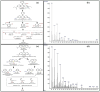
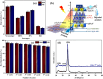
The adverse effects on human health and water supplies due to widespread use of dyes including methylene blue (MB) and rhodamine B necessitate their removal. Photocatalytic decontamination offers an alternative method which is cost effective and ecofriendly compared to other costly dye removal processes. The combination of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and cellulose from readily available modified banana leaves (MBLC) has not been explored for color degradation. The present work investigates the application of a promising g-C3N4-MBLC composite for the photocatalytic removal of methylene blue and rhodamine B dyes. The two-component hybrid composite was synthesized utilizing the one-pot in situ thermal polymerization techniques. Furthermore, multiple analytical methods were exploited to comprehensively assess the structural and morphological characteristics of the synthesized g-C3N4-cellulose hybrid composite. The composites exhibited photocatalytic activity, successfully degrading 93.35% of RhB and 92.06% (30 mg L-1) of MB dyes within 120 minutes under visible irradiation. Analysis of scavenging effects indicated that ˙O2 - and h+ radicals were the primary reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsible for the photodegradation of the dyes. Additionally, the synthesized composite showed excellent reusability, maintaining 81% efficiency after five consecutive cycles, highlighting its potential for practical applications, particularly in pollutant removal.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mustafa S. Bhatti H. N. Maqbool M. Iqbal M. Microalgae biosorption, bioaccumulation and biodegradation efficiency for the remediation of wastewater and carbon dioxide mitigation: Prospects, challenges and opportunities. J. Water Process Eng. 2021;41:102009.
-
- Hairom N. H. H. Soon C. F. Mohamed R. M. S. R. Morsin M. Zainal N. Nayan N. Zulkifli C. Z. Harun N. H. A review of nanotechnological applications to detect and control surface water pollution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021;24:102032.
-
- Getu A. Sahu O. Removal of Reactive Dye using Activated Carbon from Agricultural Waste. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2014;2:23.
-
- Lin S. Hasi W.-L.-J. Lin X. Han S. Lou X.-T. Yang F. Lin D.-Y. Lu Z.-W. Rapid and sensitive SERS method for determination of Rhodamine B in chili powder with paper-based substrates. Anal. Methods. 2015;7:5289–5294.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

