An update on renal tubular injury as related to glycolipid metabolism in diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 40303925
- PMCID: PMC12038058
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1559026
An update on renal tubular injury as related to glycolipid metabolism in diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
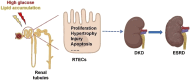
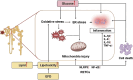
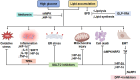
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a severe microvascular complication of diabetes, which can result in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). As the main site of renal reabsorption and its exposed environment, renal tubules can be damaged by various factors. Recent studies have shown that renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs) injury plays an important role in the occurrence and progression of DKD. The glycolipid metabolism disorders are a vital factor contributing to RTECs injury, which in turn affects the progression of DKD. Abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism can cause oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, cell apoptosis and lipid accumulation, which can cause RTECs injury. Therefore, this review describes the main pathological mechanism of the injury caused by glycolipid metabolism and the corresponding therapeutic drugs in the clinical treatment of DKD.
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; renal tubular epithelial cells; therapeutic medications.
Copyright © 2025 Feng, Yin, Xu, Zhang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis was involved in the alleviation of Jujuboside A on diabetic kidney disease-associated renal tubular injury via YY1/PGC-1α signaling.Phytomedicine. 2025 Mar;138:156411. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156411. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39884075
-
Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 promotes diabetic renal tubular injury in mice by rewiring fatty acid metabolism through SIRT1/ChREBP pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Feb;45(2):366-377. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01160-0. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37770579 Free PMC article.
-
Tubular injury in diabetic kidney disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic perspectives.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 2;14:1238927. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1238927. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37600689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mitochondria-Targeted Metabolic Tubular Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(2):156-171. doi: 10.33594/000000011. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30816665 Clinical Trial.
-
Research progress on extracellular vesicles in the renal tubular injury of diabetic kidney disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 4;14:1257430. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1257430. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37732129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting ion channel networks in diabetic kidney disease: from molecular crosstalk to precision therapeutics and clinical innovation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 26;12:1607701. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1607701. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40641971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed A. A., Mohamed S. K., Nofal S., El Morsy E. M., Ahmed A. A. E. (2023). Effect of bempedoic acid on angiotensin-II induced hypertension and vascular tissue remodelling in renal hypertensive rats through AMPK multiple signalling pathways modulation. Life Sci. 320, 121573. 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121573 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antar S. A., Abdo W., Taha R. S., Farage A. E., El-Moselhy L. E., Amer M. E., et al. (2022). Telmisartan attenuates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, and upregulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 291, 120260. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120260 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

