Focusing on Rare Variants Related to Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young in Children
- PMID: 40303944
- PMCID: PMC12017003
- DOI: 10.1155/pedi/8155443
Focusing on Rare Variants Related to Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young in Children
Abstract
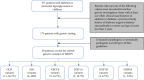
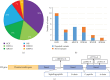
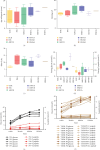
Background: In this study, we analysed the clinical and genetic characteristics and follow-up data of patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Methods: From January 2015 to December 2022, patients with persistent hyperglycaemia suspected of having monogenic diabetes or diabetes syndrome were recruited, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) was performed at the Shanghai Children's Medical Center. Patients' clinical and laboratory findings were recorded preceding follow-ups. Candidate variants were verified using Sanger sequencing. Variant pathogenicity was evaluated according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines. Results: Genetic testing was performed in 175 children. MODY-related pathogenic or likely pathogenic gene variants were identified in 30 patients from different families. Of these, 11 were diagnosed with GCK-MODY (36.7%), six with INS-MODY (20%), five with HNF1A-MODY (16.7%), five with ABCC8-MODY (16.7%), two with HNF1B-MODY (6.7%) and one with HNF4A-MODY (3.3%). There was one shift variant and seven splice-site variants, and the rest were missense variants. We discovered six novel variants. Of the 30 patients, 63.3% had a family history of diabetes, 13.3% had diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and 16.7% had positive diabetes-associated autoantibodies. The diabetes phenotype of patients with the INS variant was similar to that of patients with type 1 diabetes. All patients, including those having positive autoantibodies, required long-term insulin therapy during follow-ups. Four patients with the ABCC8 variant were unable to switch to oral sulfonylurea therapy and continued insulin therapy. Conclusion: Genetic testing is helpful for the precise diagnosis and treatment of patients with MODY, including those with DKA history and positive diabetes autoantibody. GCK-MODY is the most common type of MODY, and patients with INS variant account for a relatively large proportion of MODY cases in our cohort.
Keywords: MODY; childhood; next-generation sequencing; rare subtypes.
Copyright © 2025 Yu Ding et al. Pediatric Diabetes published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Heuvel-Borsboom H., de Valk H. W., Losekoot M., Westerink J. Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young: Seek and You Will Find. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine . 2016;74(5):193–200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

