cGAMP-targeting injectable hydrogel system promotes periodontal restoration by alleviating cGAS-STING pathway activation
- PMID: 40303968
- PMCID: PMC12038443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.02.010
cGAMP-targeting injectable hydrogel system promotes periodontal restoration by alleviating cGAS-STING pathway activation
Abstract
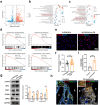
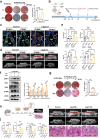
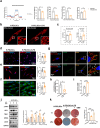
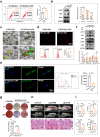
The impaired function of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) impedes restoration of periodontal tissues. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway is an innate immune pathway that sensing cytosolic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), but its role in regulating the function of PDLSCs is still unclear. In this study, we found that mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) was released into the cytoplasm through the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) in PDLSCs upon inflammation, which binds to cGAS and activated the STING pathway by promoting the production of cGAMP, and ultimately impaired the osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs. Additionally, it is first found that inflammation can down-regulate the level of the ATP-binding cassette membrane subfamily member C1 (ABCC1, a cGAMP exocellular transporter) and ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1, a cGAMP hydrolase), which further aggravated the accumulation of intracellular cGAMP, leading to the persistent activation of the cGAS-STING pathway and thus the impaired the differentiation capacity of PDLSCs. Furthermore, we designed a hydrogel system loaded with a mPTP blocker, an ABCC1 agonist and ENPP1 to promote periodontal tissue regeneration by modulating the production, exocytosis, and clearance of cGAMP. In conclusion, our results highlight the profound effects, and specific mechanisms, of the cGAS-STING pathway on the function of stem cells and propose a new strategy to promote periodontal tissue restoration based on the reestablishment of cGAMP homeostasis.
Keywords: Inflammatory environment; Injectable hydrogel system; Osteogenic differentiation; Periodontal ligament stem cells; cGAMP homeostasis; cGAS-STING pathway.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Rosier B.T., Marsh P.D., Mira A. Resilience of the oral microbiota in Health: mechanisms that prevent dysbiosis. J. Dent. Res. 2018;97(4):371–380. - PubMed
-
- Lei F., et al. Treatment of inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis by stem cell-derived exosomes. Acta Biomater. 2022;141:333–343. - PubMed
-
- Zhai Q., et al. Dental stem cell and dental tissue regeneration. Front. Med. 2019;13(2):152–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

