Potential immunomodulatory effects of the extract from Artemisia frigida Willd on loaches infested with Aeromonas hydrophila revealed by microRNA analysis
- PMID: 40303977
- PMCID: PMC12037634
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1584539
Potential immunomodulatory effects of the extract from Artemisia frigida Willd on loaches infested with Aeromonas hydrophila revealed by microRNA analysis
Abstract
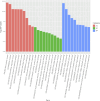
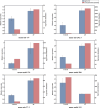
Artemisia frigida Willd is the most widely distributed Artemisia plant in the steppe and has a long history of medicinal applications in folk, especially as Mongolian medicine. Modern pharmacological research shows it exhibites biological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial. However, antibacterial applications of A. frigida in fish have not been reported. Loach is a kind of small economic fish with delicious meat and high nutritional value, which has high market value and demand in China. Nowadays, loach aquaculture technology is more mature, but the effective prevention and control of bacterial infectious disease outbreaks still need to be solved, for example, infection with Aeromonas hydrophila can cause high prevalence and mass deaths, leading to huge economic losses. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate many biological processes, including an important regulatory role in the antibacterial immune response in fish, and immune-associated miRNAs have now been identified in a wide range of fish species, but less research has been carried out on loach miRNAs. To identify miRNAs related to antibacterial immunity in loach and to understand the potential immunomodulatory mechanism of A. frigida, we infected both Artemisia-fed and non-Artemia-fed loaches with Aeromonas hydrophila, and then constructed two small RNA libraries using high-throughput sequencing technology. Bioinformatics analysis identified 924 and 923 conserved miRNAs in control and AF (Artemisia frigida) treated samples, respectively, and 30 (26 upregulated and 4 downregulated) differentially expressed miRNAs were screened. Six immune-related miRNAs were selected for fluorescence quantitative PCR used to verify the accuracy of the sequencing results. Further target gene prediction and functional analysis of 30 differential miRNAs showed that the target genes of these miRNAs were involved in the regulation of several innate and antibacterial immunity-related pathways, including endocytosis, apoptosis, phosphatidylinositol signaling system, RLR signaling pathway, TLR signaling pathway and NLR signaling pathway. This study helps to deepen the understanding of the mechanism of miRNA regulation of antibacterial immune response in loach, and provides new insights into the application of the Chinese herb A. frigida in fish.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila infection; Artemisia frigida Willd; immune regulation; loach; microRNA.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Qiu, Dai and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune mechanism of n-butanol extract of Clerodendrum bungei against loach infected with Aeromonas hydrophila.Front Immunol. 2025 May 1;16:1597463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1597463. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40375996 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating effect of vine tea on Aeromonas hydrophila infection revealed by small RNA transcriptome analyses of loach liver.Front Immunol. 2025 May 21;16:1584985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584985. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40469308 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-seq analysis of spleen and head kidney tissue from aquacultured largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in response to Aeromonas hydrophila infection.Funct Integr Genomics. 2021 Jan;21(1):101-111. doi: 10.1007/s10142-020-00763-8. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Funct Integr Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33442859
-
Research progress on the regulation of nutrition and immunity by microRNAs in fish.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Jun;113:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33766547 Review.
-
miRNAs associated with immune response in teleost fish.Dev Comp Immunol. 2017 Oct;75:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2017.02.023. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28254620 Review.
References
-
- Abdelhamed H., Ibrahim I., Nho S. W., Banes M. M., Wills R. W., Karsi A., et al. (2017). Evaluation of three recombinant outer membrane proteins, OmpA1, Tdr, and TbpA, as potential vaccine antigens against virulent Aeromonas hydrophila infection in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Fish. Shellfish immunol. 66, 480–486. 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.043 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdul Kari Z., Wee W., Mohamad Sukri S. A., Che Harun H., Hanif Reduan M. F., Irwan Khoo M., et al. (2022). Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: a mini-review. Front. Vet. Sci. 9, 1023784. 10.3389/fvets.2022.1023784fvets.2022.1023784 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed M. S., Aurpa T. T., Azad Md.A. K. (2022). Fish disease detection using image based machine learning technique in aquaculture. J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci. 34, 5170–5182. 10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.05.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

