SNRPB2: a prognostic biomarker and oncogenic driver in esophageal cancer via β-catenin/c-Myc signaling
- PMID: 40303992
- PMCID: PMC12037380
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1536473
SNRPB2: a prognostic biomarker and oncogenic driver in esophageal cancer via β-catenin/c-Myc signaling
Abstract
Background: The SNRPB2 gene encodes Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Polypeptide B2, a crucial component involved in RNA splicing processes. While SNRPB2 dysregulation has been observed in various cancers, its role in esophageal cancer (ESCA) remains unclear.
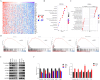
Methods: The mRNA level of SNRPB2 in ESCA was evaluated in combination with TCGA, GTEX, and GEO databases. The prognostic value of SNRPB2 was assessed using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was employed to confirm the expression of the SNRPB2 protein in tumor tissues from clinical samples. The biological functions of SNRPB2 were assessed in vitro cell assay and in vivo tumor models. The molecular mechanisms were determined by correlation and gene set enrichment analysis. Western blot experiments validated involvement in signaling pathways.
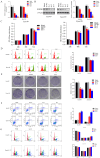
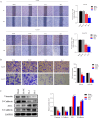
Results: Our findings unveiled that SNRPB2 was upregulated at both mRNA and protein levels in ESCA, which was associated with the pathological progression of the disease. Additionally, SNRPB2 served as a robust prognostic biomarker, implicated in driving oncogenic functions in ESCA. It facilitated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, transitioned the cell cycle, and inhibited apoptosis. Mechanistically, SNRPB2 activated genes associated with the β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway, such as β-catenin, c-Myc, CCNA2, CCNB1, CDK1, and CDK2. This activation also regulated the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), thereby facilitating the progression of ESCA.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that SNRPB2 contributes to ESCA progression by regulating the β-catenin/c-Myc axis, suggesting its potential as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for ESCA patients.
Keywords: EMT; SNRPB2; esophageal cancer; prognostic marker; β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2025 Bao, Tian, Pan, Guo, Yang, Gan and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors assert that they do not have any known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have been perceived to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

