The Role of IL-6 in Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 40305179
- PMCID: PMC12024898
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15040470
The Role of IL-6 in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
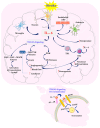
The pathophysiology of a stroke is a complex process involving oxidative stress and inflammation. As a result of the actions of reactive oxygen species (ROS), not only does vascular damage occur, but the brain tissue is also damaged. It is a dynamic process, induced by a cellular-molecular immune response, focused on the development of an immediate reaction. During ischemia, inflammatory mediators are released, among which IL-6 plays a particularly important role in the acute phase of a stroke. Recently, a lot of attention has been devoted to this pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine, which enhances the migration of leukocytes and is controlled by chemokines and the expression of adhesion handlers. The impact of IL-6 on the severity of neurological treatment and on patient prognosis in AIS is of interest to many researchers. More and more data indicate that it may be a reliable prognostic factor in strokes.
Keywords: biomarker; interleukin 6; ischemic stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Prognostic value of blood interleukin-6 in the prediction of functional outcome after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Pawluk H., Grześk G., Kołodziejska R., Kozakiewicz M., Woźniak A., Grzechowiak E., Szumny M., Sobolewski P., Bieniaszewski L., Kozera G. Effectof IL-6 and hsCRP serum levels on functional prognosis in stroke patients undergoing IV- thrombolysis: Retrospective analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2020;6:1295–1303. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S258381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pawluk H., Kołodziejska R., Grześk G., Woźniak A., Kozakiewicz M., Kosinska A., Pawluk M., Grzechowiak E., Wojtasik J., Kozera G. Increased oxidative stress markers in Acute Ischemic Stroke patients treated with thrombolytics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:15625. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415625. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Žitňanová I., Šiarnik P., Kollár B., Chomová M., Pazderová P., Andrezálová L., Ježovičová M., Koňariková K., Laubertová L., Krivošíková Z., et al. Oxidative stress markers and their dynamic changes in patients after acute ischemic stroke oxidative. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016;2016:9761697. doi: 10.1155/2016/9761697. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

