Calcium-Sensing Receptor as a Novel Target for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 40305220
- PMCID: PMC12025166
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15040509
Calcium-Sensing Receptor as a Novel Target for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
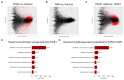
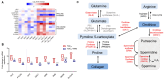
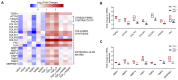
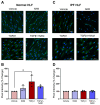
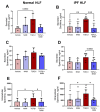
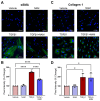
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a disease with a poor prognosis and no curative therapies. Fibroblast activation by transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) and disrupted metabolic pathways, including the arginine-polyamine pathway, play crucial roles in IPF development. Polyamines are agonists of the calcium/cation-sensing receptor (CaSR), activation of which is detrimental for asthma and pulmonary hypertension, but its role in IPF is unknown. To address this question, we evaluated polyamine abundance using metabolomic analysis of IPF patient saliva. Furthermore, we examined CaSR functional expression in human lung fibroblasts (HLFs), assessed the anti-fibrotic effects of a CaSR antagonist, NPS2143, in TGFβ1-activated normal and IPF HLFs by RNA sequencing and immunofluorescence imaging, respectively; and NPS2143 effects on polyamine synthesis in HLFs by immunoassays. Our results demonstrate that polyamine metabolites are increased in IPF patient saliva. Polyamines activate fibroblast CaSR in vitro, elevating intracellular calcium concentration. CaSR inhibition reduced TGFβ1-induced polyamine and pro-fibrotic factor expression in normal and IPF HLFs. TGFβ1 directly stimulated polyamine release by HLFs, an effect that was blocked by NPS2143. This suggests that TGFβ1 promotes CaSR activation through increased polyamine expression, driving a pro-fibrotic response. By halting some polyamine-induced pro-fibrotic changes, CaSR antagonists exhibit disease-modifying potential in IPF onset and development.
Keywords: TGFβ1; arginine–polyamine pathway; calcium/cation-sensing receptor; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; negative allosteric modulator.
Conflict of interest statement
Rupert Ecker is co-founder and CEO of the for-profit company TissueGnostics GmbH, which used to be a beneficiary in the EU-funded Marie–Sklodowska–Curie Innovative Training Network “CaSR Biomedicine” (Grant Agreement No 675228), which contributed to this publication. John Simpson is the lead investigator on grants with Clinigen, Aerogen, and Partner Therapeutics as co-applicants, and a co-applicant on a grant with Partner Therapeutics as a co-applicant. He has previously been an applicant on grants with Becton Dickinson as co-applicants. He is the Director of an NIHR Healthtech Research Centre that works with companies across the diagnostics industry.
Figures


References
-
- Adegunsoye A., Oldham J.M., Bellam S.K., Montner S., Churpek M.M., Noth I., Vij R., Strek M.E., Chung J.H. Computed Tomography Honeycombing Identifies a Progressive Fibrotic Phenotype with Increased Mortality across Diverse Interstitial Lung Diseases. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019;16:580–588. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201807-443OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raghu G., Rochwerg B., Zhang Y., Garcia C.A.C., Azuma A., Behr J., Brozek J.L., Collard H.R., Cunningham W., Homma S., et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015;192:e3–e19. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201506-1063ST. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

