Biogenic Amine Metabolism and Its Genetic Variations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comprehensive Overview
- PMID: 40305279
- PMCID: PMC12025284
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15040539
Biogenic Amine Metabolism and Its Genetic Variations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
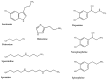
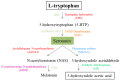
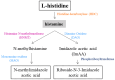
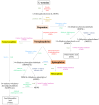
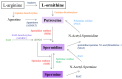
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a genetically heterogeneous syndrome characterized by repetitive, restricted, and stereotyped behaviors, along with persistent difficulties with social interaction and communication. Despite its increasing prevalence globally, the underlying pathogenic mechanisms of this complex neurodevelopmental disorder remain poorly understood. Therefore, the identification of reliable biomarkers could play a crucial role in enabling early screening and more precise classification of ASD subtypes, offering valuable insights into its physiopathology and aiding the customization of treatment or early interventions. Biogenic amines, including serotonin, histamine, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and polyamines, are a class of organic compounds mainly produced by the decarboxylation of amino acids. A substantial portion of the genetic variation observed in ASD has been linked to genes that are either directly or indirectly involved in the metabolism of biogenic amines. Their potential involvement in ASD has become an area of growing interest due to their pleiotropic activities in the central nervous system, where they act as both neurotransmitters and neuromodulators or hormones. This review examines the role of biogenic amines in ASD, with a particular focus on genetic alterations in the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; biogenic amines; metabolism; neurodevelopmental disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2022.
-
- Micai M., Fatta L.M., Gila L., Caruso A., Salvitti T., Fulceri F., Ciaramella A., D’Amico R., Del Giovane C., Bertelli M., et al. Prevalence of co-occurring conditions in children and adults with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023;155:105436. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105436. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maenner M.J., Warren Z., Williams A.R., Amoakohene E., Bakian A.V., Bilder D.A., Durkin M.S., Fitzgerald R.T., Furnier S.M., Hughes M.M., et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2023;72:1–14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

