Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfections Using Nucleocapsid Antibody Boosting
- PMID: 40305355
- PMCID: PMC12044254
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3105.250021
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfections Using Nucleocapsid Antibody Boosting
Abstract
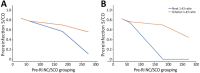
More than 85% of US adults had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 by the end of 2023. Continued serosurveillance of transmission and assessments of correlates of protection require robust detection of reinfections. We developed a serologic method for identifying reinfections in longitudinal blood donor data by assessing nucleocapsid (N) antibody boosting using a total immunoglobulin assay. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis yielded an optimal ratio of >1.43 (sensitivity 87.1%, specificity 96.0%). When prioritizing specificity, a ratio of >2.33 was optimal (sensitivity 75.3%, specificity 99.3%). In donors with higher anti-N reactivity levels before reinfection, sensitivity was reduced. Sensitivity could be improved by expanding the dynamic range of the assay through dilutional testing, from 38.8% to 66.7% in the highest reactivity group (signal-to-cutoff ratio before reinfection >150). This study demonstrated that longitudinal testing for N antibodies can be used to identify reinfections and estimate total infection incidence in a blood donor cohort.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; blood donors; respiratory infections; serology; serosurveillance; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures


References
-
- Stone M, Di Germanio C, Wright DJ, Sulaeman H, Dave H, Fink RV, et al.; NHLBI Recipient Epidemiology and Donor Evaluation Study-IV-Pediatric (REDS-IV-P). Use of US blood donors for national serosurveillance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibodies: basis for an expanded national donor serosurveillance program. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;74:871–81. 10.1093/cid/ciab537 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

