Comprehensive Survival Analysis of Alveolar Echinococcosis Patients, University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 1973-2022
- PMID: 40305427
- PMCID: PMC12044251
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3105.241608
Comprehensive Survival Analysis of Alveolar Echinococcosis Patients, University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 1973-2022
Abstract
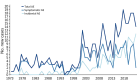
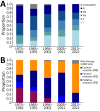
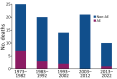
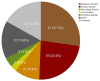
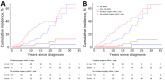
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is a zoonotic disease of increasing concern worldwide. Before benzimidazole drug therapy, 10-year death rates were 90% without surgical resection. In unresectable patients, long-term benzimidazole therapy is highly effective in stabilizing the disease course. We performed a retrospective study of 334 AE patients treated at the University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, during 1973-2022. Annual diagnoses increased over time, and more cases were detected by chance at earlier stages. Ninety patients died, mostly from causes unrelated to AE. Relative survival of AE patients compared with the population of Switzerland demonstrated a steady decrease 5 years after diagnosis. Patient age at diagnosis was the primary variable associated with overall survival. In a propensity-score matched survival analysis, early curative surgery was associated with overall improvement but not AE-specific survival. We conclude that survival of patients with AE is limited by non-AE causes and that early curative surgery does not improve AE-specific survival.
Keywords: Alveolar echinococcosis; Echinococcus multilocularis; Switzerland,; Zurich; albendazole; benzimidazole; mebendazole; mortality; parasites; relative survival; resection; surgery; survival.
Figures

References
-
- Deibel A, Meyer Zu Schwabedissen C, Husmann L, Grimm F, Deplazes P, Reiner CS, et al. Characteristics and clinical course of alveolar echinococcosis in patients with immunosuppression-associated conditions: a retrospective cohort study. Pathogens. 2022;11:441. 10.3390/pathogens11040441 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

