Self-reported COVID-19 severity among persons with tuberculosis infection in western Kenya, 2021
- PMID: 40305503
- PMCID: PMC12043119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0004372
Self-reported COVID-19 severity among persons with tuberculosis infection in western Kenya, 2021
Abstract
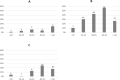
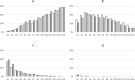
Whilst a quarter of the world's population is estimated to be infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it is unknown whether TB infection (TBI) increases the risk of severe COVID-19, which is relevant in TB-endemic settings, especially where HIV co-infection is also common. A convenience cohort of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients aged 8-80 years in western Kenya was followed daily for 14 days to assess disease progression using the validated inFLUenza-Patient-Reported-Outcome Plus signs and symptom tool. Nasal swabbing for SARS-CoV-2 was conducted to confirm the virus using polymerase chain reaction. QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus was used to diagnose TBI. HIV status was based on self-reports. Between January 3, 2021, and January 20, 2022, 373 out of 387 participants had conclusive QuantiFERON results. At baseline, 5.9% (22/373) had self-reported severe COVID-19, 33.2% (124/373) had TBI, and 11.1% (38/341) reported being HIV-infected. Median follow-up of the cohort was 105 days (range 0-368). Self-reported severe COVID-19 was experienced by 10 of 124 (8.1%) participants compared with 12 of 249 (4.8%) without TBI (odds ratio [OR] 1.73, 95% CI 0.73-4.12, p = 0.21). HIV was not associated with self-reported severe COVID-19 (OR 3.13, 0.96-8.77, p = 0.039, adjusted OR 2.77, 95%CI 0.84-7.93, p = 0.070), but age ≥ 50 years was associated with self-reported severe COVID-19 (OR 3.73, 1.47-9.07, p = 0.004, adjusted OR 2.91, 95%CI 1.02-7.69, p = 0.035). One participant died of COVID-19 three days after diagnosis, and another participant developed active TB 128 days after his COVID-19 diagnosis and was successfully treated. Both were QuantiFERON positive. Self-reported severe COVID-19 was associated with older age and not TBI. Our finding that increased age was associated with self-reported severe COVID-19 is consistent with findings in multiple settings around the world.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report. Geneva; 2017.
-
- Cohen A, Mathiasen VD, Schon T, Wejse C. The global prevalence of latent tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(3). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. . Global Tuberculosis Report. Geneva; 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
