scRNA-seq reveals an immune microenvironment and JUN-mediated NK cell exhaustion in relapsed T-ALL
- PMID: 40306275
- PMCID: PMC12147915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102098
scRNA-seq reveals an immune microenvironment and JUN-mediated NK cell exhaustion in relapsed T-ALL
Abstract
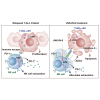
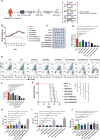
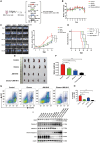
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by a high relapse rate. By single-cell transcriptome analysis, we characterize the bone marrow immune microenvironment in patients with T-ALL, identifying 13 major cell clusters. These patients exhibited abnormally expanded hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs), immunosuppressive traits in CD4+ T, CD8+ T, and natural killer (NK) cells. Subdividing CD4+ T cells reveal two subsets transitioning between T helper (Th)1/Th2, Annexin-A1 (ANXA1)-GATA3-CD4+ T, and ANXA1+GATA3+CD4+ T. Additionally, NK cells demonstrate exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment of patients with relapsed T-ALL, with JUN identified as a critical factor. Additionally, JUN is also highly expressed in T-ALL and is crucial for maintaining its proliferation. The JUN inhibitor exhibited successful lethality toward leukemia cells and ameliorated NK cell exhaustion in relapsed T-ALL cell line, as well as in cell-derived tumor xenograft (CDX), patient-derived tumor xenograft (PDX), and NOTCH1-mutant mouse models. In summary, our findings enhance the understanding of T-ALL relapse mechanisms and support the development of innovative immunotherapies for patients with relapsed T-ALL.
Keywords: JUN; NK cells; T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; immune exhaustion; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

