SinoMAKS-protocol of a randomised controlled trial to evaluate the Chinese version of the non-pharmacological, multimodal MAKS intervention for people with mild to moderate dementia in Chinese nursing homes
- PMID: 40306986
- PMCID: PMC12049968
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093618
SinoMAKS-protocol of a randomised controlled trial to evaluate the Chinese version of the non-pharmacological, multimodal MAKS intervention for people with mild to moderate dementia in Chinese nursing homes
Abstract
Introduction: The prevalence of dementia is increasing, both worldwide and in China. This disease is associated with numerous restrictions for those affected but also for caregivers and society. Due to the limited effectiveness of pharmacological interventions, more research on non-pharmacological interventions is needed. For the non-pharmacological multimodal MAKS (M: motor training, A: activities of daily living training, K: cognitive training, S: social-communicative setting) intervention, positive effects on cognition, activities of daily living, and the occurrence of behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia were identified in two randomised controlled trials in different settings in Germany. Thus, the German MAKS intervention was culturally adapted for China and will now be tested for its efficacy in Chinese nursing homes in a randomised controlled trial.
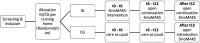
Methods and analysis: Participants will be residents of Chinese nursing homes in Shenyang, Nanjing and Dalian, fulfilling the ICD-10 criteria for Alzheimer's dementia, the psychometric criteria for mild to moderate dementia (MMSE 10-23) and none of the exclusion criteria. With n=200, effects with an effect size of Cohen's d=0.45 and a power of 1-β = 0.80 can be detected. Screening and data collection at baseline, t6 and t12 will be conducted via face-to-face contact by proxy raters in the nursing homes (i.e., trained nursing staff not involved in the intervention) and master students as external testers for the performance tests on cognition and activities of daily living. Participants will be randomly allocated to the intervention or control group. SinoMAKS (i.e., the Chinese version of the MAKS intervention) will be conducted at least three times a week for six months by trained MAKS therapists. The control group will receive care as usual for 12 months after baseline. Thus, the treatment phase is six months with follow-ups after six and 12 months after baseline. In the open phase, from t6 to t12, the nursing homes are free to offer SinoMAKS to the intervention group residents. In line with international guidelines, the primary population for analysis is the intention-to-treat sample. Global cognition (measured with the Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-III) is the primary outcome. The hypotheses will be analysed using multiple linear regression with the outcome variables as dependent variables.
Ethics and dissemination: All procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty of the Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (Ref. 24-162-B) and the Ethics Committee of the China Medical University (Ref. [2024]181). Written informed consent will be obtained from all participants or-if applicable-their legal representatives. Results will be published in peer-reviewed scientific journals and conference presentations.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN10262531.
Keywords: Clinical Protocols; Cognition; Dementia; Nursing Homes; Randomized Controlled Trial.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MZ, JS and EG are involved in a Chinese company (Nanjing Nande Cognitive Health Technology Ltd, Co.) that aims to disseminate non-pharmacological therapies—involving the MAKS concept—in China. All the other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guerchet M, Prince M, Prina M. Numbers of people with dementia worldwide: An update to the estimates in the World Alzheimer Report 2015. 2020.
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International Numbers of people with dementia around the world. 2020.
-
- World Health Organization Dementia - Key Facts 2023. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical