Development of a Decellularized Urinary Bladder Matrix and Heparin-Based Cryogel for Promoting Angiogenesis
- PMID: 40307187
- PMCID: PMC12351666
- DOI: 10.1002/mabi.202500028
Development of a Decellularized Urinary Bladder Matrix and Heparin-Based Cryogel for Promoting Angiogenesis
Abstract
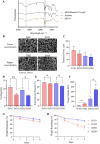
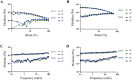
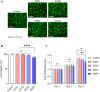
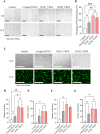
Decellularized extracellular matrix(dECM)-based scaffolds have demonstrated potential in promoting cellular migration and tissue regeneration. In this study, dECM-based cryogel scaffolds are developed with sustained vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) release properties to enhance angiogenesis in ischemic tissues. VEGF plays a critical role in angiogenesis by stimulating cell proliferation and migration, but its therapeutic delivery remains challenging due to the need for precise dosing to avoid adverse effects. Cryogels, with their microporous structure, elasticity, and shape-recovery characteristics, offer an ideal platform for controlled VEGF delivery. Using decellularized porcine urinary bladder matrix extracellular matrix (dECM) and heparin, a VEGF-releasing cryogel scaffold is fabricated. The resulting dECM/heparin cryogel is a biocompatible scaffold capable of binding VEGF and releasing it over an extended period. This platform demonstrates significant angiogenic potential both in vitro and in a murine hindlimb ischemia model, highlighting its promise for therapeutic applications in tissue regeneration.
Keywords: cryogel; decellularization; neovascularization; urinary bladder matrix; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2025 The Author(s). Macromolecular Bioscience published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heparin Functionalized Injectable Cryogel with Rapid Shape-Recovery Property for Neovascularization.Biomacromolecules. 2018 Jun 11;19(6):2257-2269. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00331. Epub 2018 May 3. Biomacromolecules. 2018. PMID: 29689163
-
Corneal Endothelium Regeneration with Decellularized Porcine Corneal Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jul;22(5):735-746. doi: 10.1007/s13770-025-00734-9. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40536661
-
Development of UROGRAFT: A Bladder Acellular Matrix-Based Composite for Advanced Cystoplasty, Highlighting the Role of Graft Shape and Composition.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Aug 11;11(8):4978-4999. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00700. Epub 2025 Jul 16. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40667861 Free PMC article.
-
Nature-Inspired Macromolecular Biocomposites Based on Decellularized Extracellular Matrix.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025 Jul;46(14):e2401049. doi: 10.1002/marc.202401049. Epub 2025 May 26. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025. PMID: 40418123 Review.
-
Unlocking the regenerative properties of extraembryonic membrane-derived biomaterials in tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2025 Sep 1;203:94-134. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.07.028. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40680916 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

