Allelic effects on KLHL17 expression underlie a pancreatic cancer genome-wide association signal at chr1p36.33
- PMID: 40307206
- PMCID: PMC12044007
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59109-2
Allelic effects on KLHL17 expression underlie a pancreatic cancer genome-wide association signal at chr1p36.33
Abstract
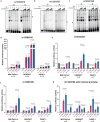
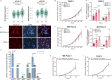
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S. Both rare and common germline variants contribute to PDAC risk. Here, we fine-map and functionally characterize a common PDAC risk signal at chr1p36.33 (tagged by rs13303010) identified through a genome wide association study (GWAS). One of the fine-mapped SNPs, rs13303160 (OR = 1.23 (95% CI 1.15-1.32), P-value = 2.74×10-9, LD r2 = 0.93 with rs13303010 in 1000 G EUR samples) demonstrated allele-preferential gene regulatory activity in vitro and binding of JunB and JunD in vitro and in vivo. Expression Quantitative Trait Locus (eQTL) analysis identified KLHL17 as a likely target gene underlying the signal. Proteomic analysis identified KLHL17 as a member of the Cullin-E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with vimentin and nestin as candidate substrates for degradation in PDAC-derived cells. In silico differential gene expression analysis of high and low KLHL17 expressing GTEx pancreas samples suggested an association between lower KLHL17 levels (risk associated) and pro-inflammatory pathways. We hypothesize that KLHL17 may mitigate cell injury and inflammation by recruiting nestin and vimentin for ubiquitination and degradation thereby influencing PDAC risk.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Allelic effects on KLHL17 expression likely mediated by JunB/D underlie a PDAC GWAS signal at chr1p36.33.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.09.16.24313748. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.16.24313748. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 30;16(1):4055. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59109-2. PMID: 39371158 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Rahib, L. et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res.74, 2913 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 75N92021D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00003/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL099355/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00004/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA210171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00005/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

