Ultra-sensitive heterojunction double gate BioTFET device for SARS-CoV-2 biomolecules detection
- PMID: 40307462
- PMCID: PMC12043985
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99817-9
Ultra-sensitive heterojunction double gate BioTFET device for SARS-CoV-2 biomolecules detection
Abstract
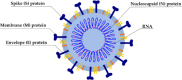
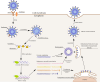
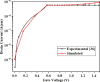
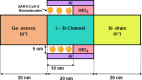
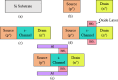
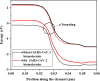
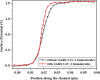
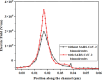
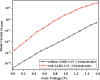
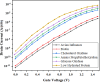
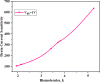
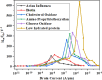
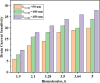
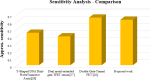
The persisting SARS-CoV-2 genetic mutation could unintentionally increase human transmission, mortality, and aggravation. Since no specific pharmaceutical therapies or vaccinations exist, rapid detection and successful treatment are essential for managing the COVID-19 pandemic. BioTFETs exhibit superior sensitivity and faster response times than bioFETs, which are more vulnerable to substantial subthreshold swing and short-channel effects. This article presents the Dielectrically Modulated-Double Gate-Heterojunction-Tunnel FET-based biosensor (DG-bioHTFET) specifically engineered to identify and detect the nucleocapsid protein and RNA biomolecules with specific permittivity (k) of SARS-CoV-2 biomolecules embedded in the nanogaps. At Vgs = 1.5 V, the proposed device achieves a drain current (Ids) of 2.32 × 10- 5 A/µm. At k = 5 and k = 3.64, the ION/IOFF ratios are 3.550 × 105 and 3.403 × 105, respectively. The data suggest that the device exhibits increased sensitivity to biomolecules possessing elevated dielectric constants. It is feasible to design ultra-sensitive TFET biosensors as a bio-recognition unit, which offers the benefits of rapid label-free detection and high sensitivity. The device exhibits superior performance in terms of high drain current with enhanced sensitivity for precise biosensing applications.
Keywords: Double gate; Heterojunction; SARS-CoV-2; Sensitivity; Tunnel field effect transistor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sreejith, S. et al. A comprehensive review on graphene FET bio-sensors and their emerging application in DNA/RNA sensingrapid Covid-19 detection. 206. 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.112202 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

