Serotonin and neurotensin inputs in the vCA1 dictate opposing social valence
- PMID: 40307550
- PMCID: PMC12137126
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08809-2
Serotonin and neurotensin inputs in the vCA1 dictate opposing social valence
Abstract
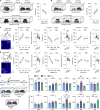
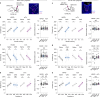
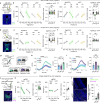
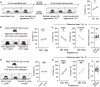
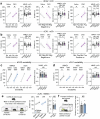
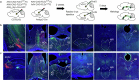
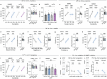
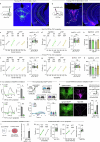
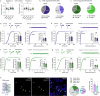
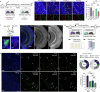
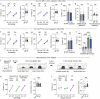
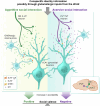
The ability to evaluate valence of a social agent based on social experience is essential for an animal's survival in its social group1. Although hippocampal circuits have been implicated in distinguishing novel and familiar conspecifics2-7, it remains unclear how social valence is constructed on the basis of social history and what mechanisms underlie the heightened valence versatility in dynamic relationships. Here we demonstrate that the ventral (v)CA1 integrates serotonin (5-HT) inputs from the dorsal raphe and neurotensin inputs from the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) to determine positive or negative valence of conspecific representations. Specifically, during an appetitive social interaction 5-HT is released into the vCA1 and disinhibits pyramidal neurons through 5-HT1B receptors, whereas neurotensin is released during an aversive social interaction and potentiates vCA1 neurons directly through NTR1s. Optogenetic silencing of dorsal raphe 5-HT and PVT neurotensin inputs into the vCA1 impairs positive and negative social valence, respectively, and excitation flexibly switches valence assignment. These results show how aversive and rewarding social experiences are linked to conspecific identity through converging dorsal raphe 5-HT and PVT neurotensin signals in the vCA1 that instruct opposing valence, and represent a synaptic switch for flexible social valence computation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

