Microglia-driven inflammation induces progressive tauopathies and synucleinopathies
- PMID: 40307569
- PMCID: PMC12130470
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01450-z
Microglia-driven inflammation induces progressive tauopathies and synucleinopathies
Abstract
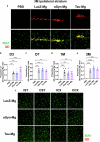
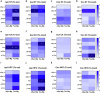
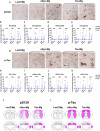
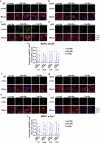
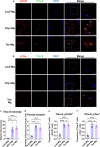
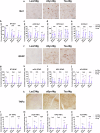
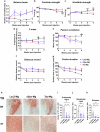
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are characterized by distinct types of abnormal protein aggregates within neurons. These aggregates are known as neurofibrillary tangles and Lewy bodies, which consist of tau and α-synuclein, respectively. As the diseases progress, these aggregates spread from one cell to another, causing protein pathology to affect broader regions of the brain. Another notable characteristic of these diseases is neuroinflammation, which occurs when microglia become activated. Recent studies have suggested that inflammation may contribute to the formation and propagation of protein aggregates. However, it remains unclear whether microglia-driven inflammation can initiate and propagate different proteinopathies and associated neuropathology in neurodegenerative diseases. Here, using single-cell RNA sequencing, we observed that microglia exposed to α-synuclein or tau underwent changes in their characteristics and displayed distinct types of inflammatory response. The naive mice that received these microglial cell transplants developed both tauopathy and synucleinopathy, along with gliosis and inflammation. Importantly, these pathological features were not limited to the injection sites but also spread to other regions of the brain, including the opposite hemisphere. In conjunction with these pathological changes, the mice experienced progressive motor and cognitive deficits. These findings conclusively demonstrate that microglia-driven inflammation alone can trigger the full range of pathological features observed in neurodegenerative diseases, and that inflammation-induced local neuropathology can spread to larger brain regions. Consequently, these results suggest that microglia-driven inflammation plays an early and pivotal role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. The transplantation of microglia activated by αSyn or tau proteins into the brains of naive mice resulted in the formation of synucleinopathy, tauopathy, gliosis, neuroinflammation and behavioral abnormalities. Activated microglia displayed alterations in subclusters as well as the corresponding feature genes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.-J.L. is a co-founder and CEO of Neuramedy Co., Ltd. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

