Gender difference in the association between serum uric acid and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 40307757
- PMCID: PMC12042553
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03917-9
Gender difference in the association between serum uric acid and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the relationship between serum uric acid (SUA) levels and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients.
Methods: We performed this retrospective research among 1087 inpatients with new-onset type 2 diabetes millitus (T2DM). Data were analyzed according to gender. Then, the populations were stratified according to their body mass index (BMI) levels in men and women, respectively. The physical and biochemical indicators were measured and recorded. The relationship between SUA and MASLD was estimated using logistic regression analysis, and the unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios (ORs) were calculated.
Results: After adjusting for age, BMI, and other components of the metabolic syndrome, SUA was independently associated with MASLD only in men, but not in women. In addition, for men, the SUA levels were independently associated with MASLD in both non-overweight/obesity and overweight/obesity group. However, for women, the SUA levels were independently related to MASLD in non-overweight/obesity group. There was no association between SUA and MASLD in women with overweight/obesity.
Conclusion: In newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients, elevated SUA is an independent predictor for the risk of MASLD in males. In females, the relationship between SUA and MASLD may depend on BMI, with significance only in non-overweight/obese individuals.
Keywords: MASLD; Serum uric acid; Sex; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki (6 th revision, 2008) as reflected in a priori approval by the ethics committees of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University Dezhou Hospital. Written informed consent was provided by each participant. Consent for publication: Informed consent for publication was obtained from each participant included in the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
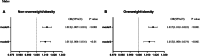

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

