Reflective mindfulness and emotional regulation training to enhance nursing students' self-awareness, understanding, and regulation: a mixed method randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40307764
- PMCID: PMC12045004
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-025-03086-w
Reflective mindfulness and emotional regulation training to enhance nursing students' self-awareness, understanding, and regulation: a mixed method randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Nursing students encounter significant academic and psychological challenges that can impede their transition from theoretical knowledge to practical application, affecting their well-being and professional development.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Reflective Mindfulness and Emotional Regulation Training (RMERT) in improving nursing students' self-awareness, understanding, and emotional regulation.
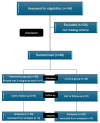
Design and methods: This study employed a convergent parallel mixed-method randomized controlled trial design. Forty fourth-year undergraduate nursing students were randomly assigned using simple randomization (computer-generated random numbers) into either an intervention group (n = 20) or a control group (n = 20). The intervention group participated in a six-week RMERT program designed to enhance self-awareness, understanding, and emotional regulation. The control group continued with standard course activities. Quantitative data were collected pre- and post-intervention using the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ) and the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale (MAAS), and analyzed using SPSS. Qualitative data, gathered exclusively from the intervention group through recorded reflective group sessions, were analyzed using thematic analysis.
Results: The intervention group exhibited significantly improved self-awareness, understanding, and emotional regulation compared to the control group. Additionally, students displayed an increased capacity for mindfulness, a decreased tendency to suppress emotions, and greater comfort in reflecting on positive and negative emotions.
Conclusion: Integrating RMERT into nursing curricula may enhance nursing students' well-being and professional growth, mainly when counseling resources are limited. The program can improve self-awareness, understanding, and regulation skills necessary for effective nursing practice.
Implication for nursing practice: Integrating RMERT into nursing curricula enhances self-awareness, emotional regulation, and reflective practice. This approach equips students with essential skills for managing clinical stress and building therapeutic relationships. As future nurses, they develop resilience, clinical reasoning, and empathetic patient care, ultimately elevating care quality and professional growth in diverse healthcare settings.
Trial registration number: The study was registered retrospectively on https://register.
Clinicaltrials: gov/ on 23 of December 2024 under the reference number: NCT06760962.
Keywords: Emotional regulation; Mindfulness; Mixed method; Nursing education; Nursing students; Randomized controlled trial; Self-awareness.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study strictly followed the guidelines and standards outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (October 2008). It was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Nursing at Benha University (REC PSYN P39/2022) in Egypt. Moreover, written informed consent was obtained from nursing students who voluntarily agreed to participate in the research. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials