Ubiquitination-mediated upregulation of glycolytic enzyme MCT4 in promoting astrocyte reactivity during neuroinflammation
- PMID: 40307809
- PMCID: PMC12042614
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03453-z
Ubiquitination-mediated upregulation of glycolytic enzyme MCT4 in promoting astrocyte reactivity during neuroinflammation
Abstract
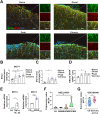
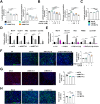
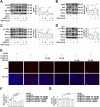
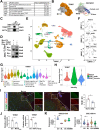
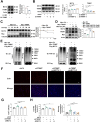
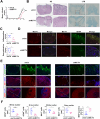
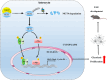
One of the histopathological hallmarks of neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) is the emergence of astrocyte reactivity. Accumulating evidence suggests that excessive glycolysis may lead to astrocyte reactivity and contribute to neuroinflammatory responses. However, the intricate mechanisms underlying astrocyte metabolic reprogramming towards glycolysis remain largely unknown. Here, we conducted in vitro experiments using primary astrocytes and in vivo studies in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS). We observed increased astrocytic expression of MCT4, a key glycolytic regulator, in EAE mice. MCT4 enhanced astrocyte reactivity through promoting glycolysis and proliferation, mediated primarily by activation of the NF-κB and c-Myc signaling pathways. Notably, we report a novel regulatory mechanism in which the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM7 regulates MCT4 levels via ubiquitination. In mice, blockade of astrocyte MCT4 expression by intracerebroventricular injection of lentivirus alleviated disease severity of EAE mice. The results suggest that targeting glycolysis, specifically through the inhibition of MCT4 expression, might be effective in reducing astrocyte reactivity, neuroinflammation and demyelination occurring in MS and relating neuroinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; Glycolysis; Proliferation; Ubiquitination.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Shaanxi Normal university (Permit Number: 2024 − 179). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

