Mapping the ADDQoL to the EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40307906
- PMCID: PMC12044720
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-025-02371-1
Mapping the ADDQoL to the EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: The Audit of Diabetes-Dependent Quality of Life (ADDQoL) is a widely used instrument for assessing quality of life in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). However, it does not directly yield health utility values essential for economic evaluations. This study developed mapping algorithms to predict EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 utility values from ADDQoL scores in T2DM patients in China.
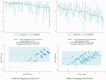
Methods: Cross-sectional data from 800 T2DM patients in China, stratified by age, sex, and geographical region, were divided into development (80%) and validation (20%) groups. Pearson correlation analyses were conducted to assess the conceptual overlap between ADDQoL and the EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2. Six predictor sets and six regression methods were explored to map ADDQoL scores to EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 utility values, respectively. Model performance was evaluated using mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
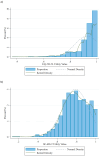
Results: For the development group, the mean (SD) ADDQoL Average Weighted Impact (AWI) score was - 2.426 (1.052), and the mean (SD) utility values for EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 were 0.928 (0.092) and 0.791 (0.133), respectively. Among all 36 alternative mapping models each for EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2, the best performance was consistently observed in the two-part models that included the ADDQoL AWI, the first overview item, and their squared terms. For the algorithm mapping to EQ-5D-5L utility values, it achieved a MAE of 0.067, a RMSE of 0.095, and an ICC of 0.414; For the algorithm mapping to SF-6Dv2 utility values, the corresponding metrics were an MAE of 0.099, an RMSE of 0.120, and an ICC of 0.517.
Conclusions: This study provides a mapping framework to estimate EQ-5D-5L and SF-6Dv2 utility values from ADDQoL scores. These algorithms could be used to support economic evaluations, specifically tailored for Chinese T2DM populations.
Keywords: ADDQoL; EQ-5D-5L; HRQoL; Mapping; SF-6Dv2; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Role of the funder: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Conflicts of interest/competing interests: No conflicts of interest were reported by the authors. Consent to participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Participants were informed about their freedom of refusal. Anonymity and confidentiality were maintained throughout the research process. Ethical approval: This study was approved by the Academic Ethics Committee at Tianjin University (No. TJUE-2023-206) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th edn [https://www.diabetesatlas.org]
-
- Hong SN, Mak IL, Chin WY, Yu EYT, Tse ETY, Chen JY, Wong CKH, Chao DVK, Tsui WWS, Lam CLK, et al. Age-specific associations between the number of co-morbidities, all-cause mortality and public direct medical costs in patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(2):454–67. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

