Case Report: Coexistence of an esophageal schwannoma disguised as a leiomyoma with a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the gastric fundus
- PMID: 40308497
- PMCID: PMC12040618
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1573436
Case Report: Coexistence of an esophageal schwannoma disguised as a leiomyoma with a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the gastric fundus
Abstract
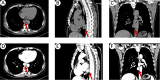
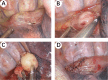
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of coexisting esophageal schwannoma and gastric fundus gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). This case report describes the diagnostic and treatment process of a patient with esophageal schwannoma who also had a concurrent gastric fundus GIST and was presented to Hebei General Hospital (Hebei, China) in October 2024. The association between the pathogenesis of the two types of submucosal gastrointestinal tumors is unclear, with limited existing evidence in the literature. The esophageal schwannoma was misdiagnosed as a leiomyoma preoperatively, which prompted us to seek new diagnostic modalities to differentiate gastrointestinal submucosal lesions (leiomyomas, GISTs, and schwannomas). Surgical resection is considered the optimal treatment for esophageal schwannoma. The patient underwent a right single-port thoracoscopic esophageal tumor resection and recovered well, subsequently being discharged smoothly from the hospital.
Keywords: case report; differential diagnosis; esophageal schwannoma; gastrointestinal stromal tumor; leiomyoma.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Xin, Wu, Hu, Jia, Zhang, Ma and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jaiswal P, Ijeli AN, Patel D, Jaiswal R, Attar BM, Devani K, et al. Esophageal schwannoma: A systematic review of 46 cases: 393. Am J Gastroenterol. (2017) 112:S209–10. doi: 10.14309/00000434-201710001-00393 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

