Association Between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 40308631
- PMCID: PMC12043021
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S491628
Association Between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
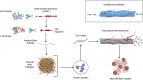
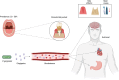
Background: Periodontitis has long been linked to various inflammatory, chronic, and immunological diseases, such as heart disease or diabetes. Recently, there has been increasing scientific interest in the bidirectional relationship that may exist between periodontitis and the presence and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD), where it is hypothesized that the infiltration of oral microorganisms (mainly Porphyromonas gingivalis) into the bloodstream, which subsequently reaches the brain, causes inflammatory and neurodegenerative processes related to AD.
Purpose: The purpose of this review is to determine the association between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Alzheimer's disease in older adults.
Patients and methods: It was carried out using different databases such as PubMed, Web of Science, among others, of no more than 10 years old focused on older adult patients who have presented periodontitis and Alzheimer's disease. MESH-indexed terms were used, getting 307 articles. After removing 206 duplicates and applying inclusion criteria (language, relevance, and contribution to the study's objectives), 24 articles were selected for analysis.
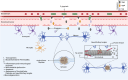
Conclusion: Evidence has been found that gingipains produced by P. gingivalis may contribute to the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain and nerve cell damage characteristic of Alzheimer's disease. It has also been observed that P. gingivalis can enter the brain and stimulate a local immune response. Although the association is promising, more research is needed to confirm it and to develop effective treatments. These findings may have significant implications for clinical practice, potentially leading to preventive or therapeutic strategies targeting oral health as a modifiable risk factor for AD. Further research could focus on exploring these pathways and developing targeted interventions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Porphyromonas gingivalis; older adults; periodontitis.
© 2025 Sarmiento-Ordóñez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Porphyromonas gingivalis Infections Increase the Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2023 Jan 18;21:7-16. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.b3818045. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2023. PMID: 36651311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease and Porphyromonas gingivalis: Exploring the Links.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;15(1):96. doi: 10.3390/life15010096. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Aspects of Periodontitis and Alzheimer's Disease-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 23;25(5):2612. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052612. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of periodontal bacteria, Porphyromonas Gingivalis, in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and aggravation: a review.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021 May-Jun;35(3 Suppl. 1):37-45. doi: 10.23812/21-3supp1-6. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021. PMID: 34289663 Review.
-
Porphyromonas Gingivalis as a Risk Factor to Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021 Sep 13;5(1):721-732. doi: 10.3233/ADR-200237. eCollection 2021. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34755046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel R. The State of Oral Health in Europe Report Commissioned by the Platform for Better Oral Health in Europe. 2012.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources