Genomic prediction and QTL analysis for grain Zn content and yield in Aus-derived rice populations
- PMID: 40308942
- PMCID: PMC12037680
- DOI: 10.1007/s13562-024-00886-0
Genomic prediction and QTL analysis for grain Zn content and yield in Aus-derived rice populations
Abstract
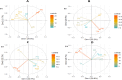
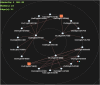
Zinc (Zn) biofortification of rice can address Zn malnutrition in Asia. Identification and introgression of QTLs for grain Zn content and yield (YLD) can improve the efficiency of rice Zn biofortification. In four rice populations we detected 56 QTLs for seven traits by inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM), and 16 QTLs for two traits (YLD and Zn) by association mapping. The phenotypic variance (PV) varied from 4.5% (qPN 4.1 ) to 31.7% (qPH 1.1 ). qDF 1.1 , qDF 7.2 , qDF 8.1 , qPH 1.1 , qPH 7.1 , qPL 1.2 , qPL 9.1, qZn 5.1 , qZn 5.2 , qZn 6.1 and qZn 7.1 were identified in both dry and wet seasons; qZn 5.1 , qZn 5.2 , qZn 5.3, qZn 6.2, qZn 7.1 and qYLD 1.2 were detected by both ICIM and association mapping. qZn 7.1 had the highest PV (17.8%) and additive effect (2.5 ppm). Epistasis and QTL co-locations were also observed for different traits. The multi-trait genomic prediction values were 0.24 and 0.16 for YLD and Zn respectively. qZn 6.2 was co-located with a gene (OsHMA2) involved in Zn transport. These results are useful for Zn biofortificatiton of rice.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13562-024-00886-0.
Keywords: GWAS; Genes; QTL; RIL; Rice; Yield; Zn.
© The Author(s) 2024, corrected publication 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Aggett PJ (2020) Chapter 22: Iron. In: Marriott BP, Birt DF, Stallings VA, Yates AABT (eds) Present knowledge in nutrition, 11th edn. Academic Press, London, pp 375–392
-
- Arfi N, Khatoon K, Alim F (2022) Zinc malnutrition in children and its consequences on health. In: Tabrez S, Khan AM (eds) Microbial biofertilizers and micronutrient availability: the role of zinc in agriculture and human health. Springer, Cham, pp 35–67. 10.1007/978-3-030-76609-2_2
-
- Ata-Ul-Karim ST, Begum H, Lopena V, Borromeo T, Virk P, Hernandez JE, Gregorio GB, Collard BCY, Kato Y (2022) Genotypic variation of yield-related traits in an irrigated rice breeding program for tropical Asia. Crop Environ 1(3):173–181. 10.1016/j.crope.2022.08.004 - DOI
-
- Babu PM, Neeraja CN, Rathod S, Suman K, Uttam GA, Chakravartty N, Lachagari VBR, Chaitanya U, Rao LVS, Voleti SR (2020) Stable SNP allele associations with high grain zinc content in polished rice (Oryza sativa L.) identified based on ddRAD sequencing. Front Genet 11(August):1–18. 10.3389/fgene.2020.00763 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
