The potential crosstalk genes and molecular mechanisms between systemic lupus erythematosus and periodontitis
- PMID: 40309038
- PMCID: PMC12040896
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1527713
The potential crosstalk genes and molecular mechanisms between systemic lupus erythematosus and periodontitis
Abstract
Background: Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of periodontitis (PD) among patients diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, the underlying common mechanism between them remains incompletely understood. Accordingly, the aim of this study is to examine diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for SLE and PD by leveraging publicly accessible microarray datasets and transcriptome analysis.
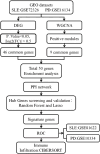
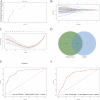
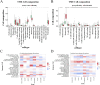
Method: Datasets pertaining to SLE and PD were retrieved from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and subsequently analyzed for differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Key gene modules were identified through weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and shared genes were obtained by overlapping key genes between DEGs and WGCNA. These shared genes were subsequently subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses, leading to the establishment of a Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network. Random forest (RF) and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (Lasso) regression were employed to identify key hub genes. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated using a new validation dataset to evaluate the performance of candidate genes. Finally, levels of immune cell infiltration in SLE and PD were assessed using CIBERSORTx.
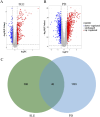
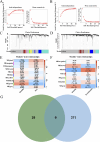
Results: A total of 50 core genes were identified between the genes screened by WGCNA and DEGs. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that these genes are primarily associated with the PI3K-Akt and B-cell receptor signaling pathways. Additionally, using machine learning algorithms and ROC curve analysis, a total of 8 key genes (PLEKHA1, CEACAM1, TNFAIP6, TCN2, GLDC, GNG7, LY96, VCAN) were identified Finally, immune infiltration analysis highlighted the significant roles of neutrophils, monocytes, plasma cells, and gammadelta T cells (γδ T cells) in the pathogenesis of both SLE and PD.
Conclusion: This study identifies 8 hub genes that could potentially serve as diagnostic markers for both SLE and PD, highlighting the importance of VCAN and LY96 in diagnosis. Moreover, the involvement of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in both diseases suggests its significant role. These identified key genes and signaling pathways lay the groundwork for deeper comprehension of the interplay between SLE and PD.
Keywords: LY96; PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; VCAN; periodontitis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Li, Zhu, Zhu, Huang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bagavant H., Dunkleberger M. L., Wolska N., Rybakowska P., Sroka M., Rasmussen A., et al. (2018). Periodontal pathogen exposure facilitates disease activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 200 (45), 45.7–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.200.Supp.45.7 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

