Annexin A: Cell Death, Inflammation, and Translational Medicine
- PMID: 40309306
- PMCID: PMC12042829
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S511439
Annexin A: Cell Death, Inflammation, and Translational Medicine
Abstract
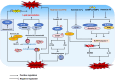
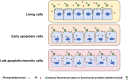
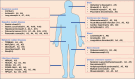
The annexin superfamily proteins, a family of calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins, are involved in a variety of Ca²+-regulated membrane events. Annexin A, expressed in vertebrates, has been implicated in a variety of regulated cell death (RCD) pathways, including apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and neutrophil extracellular trap-induced cell death (NETosis). Given that inflammation is a key driver of cell death, the roles of Annexin A in inflammation have been extensively studied. In this review, we discuss the regulatory roles of Annexin A in RCD and inflammation, the development of related targeted therapies in translational medicine, and the application of animal models to study these processes. We also analyze current challenges and discuss future directions for improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Annexin A; inflammation; regulated cell death; translational medicine.
© 2025 Qian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulated cell death (RCD) in cancer: key pathways and targeted therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 13;7(1):286. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01110-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35963853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heme Oxgenase-1, a Cardinal Modulator of Regulated Cell Death and Inflammation.Cells. 2021 Feb 28;10(3):515. doi: 10.3390/cells10030515. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated Necrotic Cell Death in Alternative Tumor Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2020 Dec 17;9(12):2709. doi: 10.3390/cells9122709. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33348858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec 8;15(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01392-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36482419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting regulated cell death (RCD) with small-molecule compounds in triple-negative breast cancer: a revisited perspective from molecular mechanisms to targeted therapies.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Apr 12;15(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01260-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35414025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Insights into Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death (ADCD): A Novel Avenue for Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2025 Jul 13;14(14):1072. doi: 10.3390/cells14141072. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Electrochemical Approaches for the Early Detection of Programmed Cell Death.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 31;10(31):34106-34122. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05652. eCollection 2025 Aug 12. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40821520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

