A window into the brain: multimodal MRI assessment of vascular cognitive impairment
- PMID: 40309660
- PMCID: PMC12040843
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1526897
A window into the brain: multimodal MRI assessment of vascular cognitive impairment
Abstract
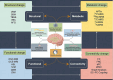
Vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) encompasses a diverse range of syndromes, including mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia (VaD), primarily attributed to cerebrovascular lesions and vascular risk factors. Its prevalence ranks second only to Alzheimer's disease (AD) in neuro diseases. The advancement of medical imaging technology, particularly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has enabled the early detection of structural, functional, metabolic, and cerebral connectivity alterations in individuals with VCI. This paper examines the utility of multimodal MRI in evaluating structural changes in the cerebral cortex, integrity of white matter fiber tracts, alterations in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and glymphatic system (GS) activity, alteration of neurovascular coupling function, assessment of brain connectivity, and assessment of metabolic changes in patients with VCI.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; dynamic functional connectivity; glymphatic system; resting-state functional MRI; structure–function coupling; vascular cognitive impairment.
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Liu, Liu, Wang, Cong, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural network efficiency mediates the association between glymphatic function and cognition in mild VCI: a DTI-ALPS study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Nov 16;14:974114. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.974114. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36466598 Free PMC article.
-
A "glympse" into neurodegeneration: Diffusion MRI and cerebrospinal fluid aquaporin-4 for the assessment of glymphatic system in Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Aug 15;45(12):e26805. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26805. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39185685 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of diffusion, perfusion and functional MRI to the disconnection hypothesis in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2018 Feb 28;3(3):131-139. doi: 10.1136/svn-2017-000080. eCollection 2018 Sep. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30294468 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and management of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002;(63):91-109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6137-1_6. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12597611 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of blood brain barrier dysfunction during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular cognitive impairment.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 16;12(4):1639-1658. doi: 10.7150/thno.68304. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35198062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bálint A. R., Puskás T., Menyhárt Á., Kozák G., Szenti I., Kónya Z., et al. . (2019). Aging impairs cerebrovascular reactivity at preserved resting cerebral arteriolar tone and vascular density in the laboratory rat. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:301. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00301, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

