The impact of internet pornography addiction on brain function: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study
- PMID: 40309664
- PMCID: PMC12040873
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1477914
The impact of internet pornography addiction on brain function: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study
Erratum in
-
Correction: The impact of internet pornography addiction on brain function: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Jul 17;19:1658882. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1658882. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40746910 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: There is extensive awareness of internet pornography addiction. It not only affects the mental health of adolescents but also promotes criminal activity. However, the impact of internet pornography addiction on functional in the brain remains unclear.
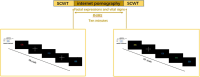
Methods: 16 healthy college students and five college students with severe internet pornography addiction were invited to participate in the experiment and watch a pornographic video. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) was used to measure the dynamic changes in hemoglobin in the brain during a 10 min session of viewing internet pornography. Participants completed the Stroop Color and Word Task (SCWT) before and after they had watched the video. Facial expressions and life signs were measured continuously during the experiment.
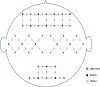
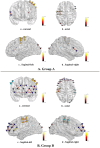
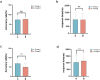
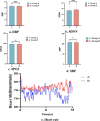
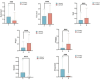
Results: Compared with the group that frequently viewed pornographic videos, the group with low-frequency pornography viewing exhibited enhanced functional connectivity in the inferior prefrontal cortex and pars triangularis of Broca's area in the frontal lobe, the primary somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe, and the pre-motor and supplementary motor cortices. Moreover, the high-frequency pornography-viewing group exhibited hyperactive parasympathetic activity, more pronounced sexual arousal, and stronger functional connectivity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and frontopolar area. After viewing the pornography, the high-frequency group demonstrated longer reaction times and significantly reduced accuracy while completing the Stroop Color and Word Test (SCWT) compared to the low-frequency group and also their own performance before and after viewing the pornography.
Discussion: This study demonstrated the hyperactive and inhibited brain areas under the impact of pornography video addiction. The results may strengthen our understanding of neurobiology and facilitate the development of prevention policies for adolescents.
Keywords: addiction; brain function; cognition; functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS); internet pornography.
Copyright © 2025 Shu, Tang, Wu, Feng, Lv, Huang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brand M., Young K., Laier C., Wölfling K., Potenza M. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: an Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 71 252–266. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Byrne A. (1995). Signs and symptoms in drug addiction. Aust. Fam. Phys. 24:420. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

