An Assessment of Oral-Health-Related Quality of Life and Anxiety in Early Adolescents (11-14 Years) at Their First Dental Visit: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40310054
- PMCID: PMC12025650
- DOI: 10.3390/children12040428
An Assessment of Oral-Health-Related Quality of Life and Anxiety in Early Adolescents (11-14 Years) at Their First Dental Visit: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
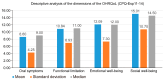
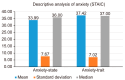
Background: Knowing the oral-health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) status of pediatric patients would be helpful in analyzing their level of dental anxiety before their first visit to a pediatric dentist. However, few studies have analyzed OHRQoL and anxiety in early adolescent patients. The aim of this study was to describe the OHRQoL and anxiety levels of early adolescents, according to age and sex, at their first dental examination. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on early adolescents (11-14 years old) attending their first dental examination in 2023-2024. OHRQoL was assessed using the Spanish version of the Child Perceptions Questionnaire 11-14 (CPQ-Esp11-14) and anxiety using the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory in Children (STAIC). Results: A total of 130 early adolescents were assessed, with an average age of 12.6 years (±1.06) and an equal sex distribution (65 boys and 65 girls). Among the analyzed sample, the OHRQoL dimension with the highest score was social well-being (15.01 ± 10.7), whereas the oral symptoms dimension (8.6 ± 4.25) had the lowest impact. There were no statistically significant differences between female and male early adolescents in the anxiety state or anxiety-trait dimensions or in the dimension of OHRQoL, except for oral symptoms, which were higher in boys (9.48 ± 4.51 versus 7.72 ± 3.81). Similarly, no significant differences were found based on age regarding anxiety or OHRQoL. Conclusions: Considering the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that higher levels of anxiety negatively impacted the OHRQoL of the early adolescent population studied.
Keywords: anxiety; early adolescents; oral-health-related quality of life; pediatric dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous