Avelumab induces greater Fc-Fc receptor-dependent natural killer cell activation and dendritic cell crosstalk compared to durvalumab
- PMID: 40311014
- PMCID: PMC12051578
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2025.2494995
Avelumab induces greater Fc-Fc receptor-dependent natural killer cell activation and dendritic cell crosstalk compared to durvalumab
Abstract
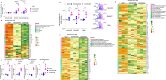
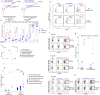
Several FDA-approved anti-PD-L1 (programmed cell death ligand-1) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are used to treat cancer. While these mAbs primarily target and intercept PD-L1:PD-1 inhibitory signaling in T-cells, the Fc-domains of these mAbs are distinct, and the unique cellular cascades triggered by differing Fc-domains of PD-L1 mAbs have not been directly investigated. In this study, we compared the innate immune effects of two widely used anti-PD-L1 IgG1 mAbs which bear distinct Fc-domains, avelumab (native-Fc) and durvalumab (mutated-Fc), using two-cell and three-cell co-culture systems containing Natural Killer cells (NK-cells), dendritic cells (DCs) and various tumor cell lines of multiple cancer origins. We show a robust enhancement in NK-cell effector function, DC maturation, reciprocal NK:DC crosstalk and DC editing that is unique to avelumab treatment using multiple functional immune assays. By transcriptomic analysis, we show for the first time pivotal differences in gene sets involved in NK-cell effector function, DC maturation, immunoregulatory interactions, and cytokine production between innate immune cells treated with avelumab versus durvalumab. Furthermore, we report several previously unknown Fc-receptor-associated biological pathways uniquely triggered by avelumab. Our findings elucidate novel mechanisms of Fc-dependent actions of PD-L1 mAbs which may inform their use in future clinical trials.
Keywords: ADCC; FCGR; Fc-domain; IgG1; PD-L1; dendritic cell maturation; immune crosstalk; immunogenomics; mabs.
Conflict of interest statement
T.A.C. is a co-founder of Gritstone Oncology and holds equity. T.A.C. holds equity in An2H. T.A.C. acknowledges grant funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Illumina, Pfizer, An2H, and Eisai. T.A.C. has served as an advisor for Bristol-Myers, MedImmune, Squibb, Illumina, Eisai, AstraZeneca, and An2H. T.A.C. is an inventor on intellectual property and patent held by MSKCC on using tumor mutation burden to predict immunotherapy response, which has been licensed to PGDx. NO, AR, VM, RMS have no potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Park JE, Kim SE, Keam B, Park H-R, Kim S, Kim M, Kim TM, Doh J, Kim D-W, Heo DS. Anti-tumor effects of NK cells and anti-PD-L1 antibody with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in PD-L1-positive cancer cell lines. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e000873. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000873. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
