Ventilatory efficiency in cardiac amyloidosis-A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40312148
- PMCID: PMC12045699
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70308
Ventilatory efficiency in cardiac amyloidosis-A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
In cardiac amyloidosis (CA) cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is underexplored. This study evaluated exercise limitations in CA using CPET, focusing on the ventilation-to-carbon dioxide production (VE/VCO2) slope and peak oxygen uptake (VO2). Seventeen studies involving 1505 patients were analyzed and systematically reviewed according to PRISMA reporting guidelines. Subgroup analyses assessed differences by diagnosis (ATTR vs. AL), CPET modality, and age. The cohort included 12% with AL, 80% with ATTR (23% hereditary [ATTRv], 70% wild-type [ATTRwt], 7% unspecified), and 8% unidentified subtypes. VE/VCO2 slope was elevated across ATTR subgroups: 38.4 (95% CI: 36.9-40.0, I2 = 57%) in ATTRwt and 37.9 (95% CI: 35.1-40.7, I2 = 70%) in ATTRv. ATTR patients were older than AL patients by 9.0 years (95% CI: 0.4-17.6, I2 = 88%) and had a higher VE/VCO2 slope: 2.5 (95% CI: 0.2-4.8, I2 = 0%). CPET modality influenced peak VO2, which was lowest for treadmill exercise (13.7, 95% CI: 12.7-14.8, I2 = 0%, mL/min/kg) compared to upright cycle ergometry (14.7, 95% CI: 14.3-15.1, I2 = 33%) and semi-recumbent cycle ergometry (14.5, 95% CI: 14.1-14.9, I2 = 28%). A high VE/VCO2 slope characterizes both ATTRwt and ATTRv, while AL patients are younger with lower VE/VCO2 slope levels. Peak VO2 in ATTR patients may depend on exercise modality.
Keywords: amyloidosis; cardiomyopathy; exercise testing; heart failure; risk prediction.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
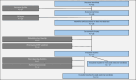
Figures


References
-
- Agostoni, P. , Corrà, U. , Cattadori, G. , Veglia, F. , la Gioia, R. , Scardovi, A. B. , Emdin, M. , Metra, M. , Sinagra, G. , Limongelli, G. , Raimondo, R. , Re, F. , Guazzi, M. , Belardinelli, R. , Parati, G. , Magrì, D. , Fiorentini, C. , Mezzani, A. , Salvioni, E. , … Passino, C. (2013). Metabolic exercise test data combined with cardiac and kidney indexes, the MECKI score: A multiparametric approach to heart failure prognosis. International Journal of Cardiology, 167(6), 2710–2718. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.06.113 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Argirò, A. , Silverii, M. V. , Burgisser, C. , Fattirolli, F. , Baldasseroni, S. , di Mario, C. , Zampieri, M. , Biagioni, G. , Mazzoni, C. , Chiti, C. , Allinovi, M. , Ungar, A. , Perfetto, F. , & Cappelli, F. (2024). Serial changes in cardiopulmonary exercise testing parameters in untreated patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 40(3), 364–369. 10.1016/j.cjca.2023.09.028 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Badr Eslam, R. , Öztürk, B. , Rettl, R. , Capelle, C. D. J. , Qin, H. , Binder, C. , Dachs, T. M. , Camuz Ligios, L. , Duca, F. , Dalos, D. , Schrutka, L. , Alasti, F. , Kastner, J. , Vila, G. , & Bonderman, D. (2022). Impact of tafamidis and optimal background treatment on physical performance in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. Circulation. Heart Failure, 15(7), e008381. 10.1161/circheartfailure.121.008381 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

