Triglyceride glucose waist circumference and non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta analysis
- PMID: 40312323
- PMCID: PMC12044922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03888-x
Triglyceride glucose waist circumference and non alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta analysis
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) plays a noticeable role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The triglyceride glucose-waist circumference (TyG-WC) index, a novel measure for assessing IR, may hold significant predictive value for NAFLD. However, the relationship between TyG-WC and the risk of NAFLD remains elusive. To investigate this association, this comprehensive meta-analysis was conducted.
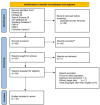
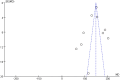
Methods: A systematic electronic search was conducted using the PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases from their inception until July 2024 to identify observational studies assessing the relationship between TyG-WC and the risk of NAFLD. Joanna Briggs Institute's critical appraisal checklist was utilized to evaluate the quality of cross-sectional studies, while the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) score was used to assess cohort studies. The principal summary outcomes included the mean difference (MD) and the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI).
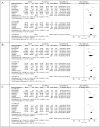
Results: In total, 10 studies comprising 38,518 participants were included in this meta-analysis, of whom 37% were diagnosed with NAFLD. The analysis revealed a significant MD between NAFLD and non-NAFLD cases (MD, 137.41; [95% CI, 121.52-153.31]).
Conclusion: A significant MD was identified between NAFLD and non-NAFLD cases. The TyG-WC index was found to be positively correlated with the risk of NAFLD, suggesting that it may serve as a potential indicator for NAFLD.
Keywords: Insulin resistance; Meta-analysis; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; TyG-WC index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
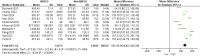
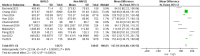
References
-
- Song R, Li Z, Zhang Y, Tan J, Chen Z. Comparison of NAFLD, MAFLD and MASLD characteristics and mortality outcomes in united States adults. Liver Int. 2024;44(4):1051–60. - PubMed
-
- Amini-Salehi E, Letafatkar N, Norouzi N, Joukar F, Habibi A, Javid M, Sattari N, Khorasani M, Farahmand A, Tavakoli S, et al. Global prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an updated review Meta-Analysis comprising a population of 78 million from 38 countries. Arch Med Res. 2024;55(6):103043. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73–84. - PubMed
-
- Papatheodoridi M, Cholongitas E. Diagnosis of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): current concepts. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(38):4574–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

