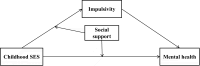
Impulsivity and social support as intervening and interactive variables in the link between childhood socioeconomic status and mental health among first-year college students
- PMID: 40313236
- PMCID: PMC12043679
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1569001
Impulsivity and social support as intervening and interactive variables in the link between childhood socioeconomic status and mental health among first-year college students
Abstract
Background: Significant attention has been given to the mental health of college students, especially first-year college students, with childhood socioeconomic status (SES) identified as a key factor. This study investigated the correlation of impulsivity and social support in the relationship between childhood SES and current mental health, with a focus on depressive and anxiety symptoms, in first-year college students.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was designed, surveying 6,378 first-year students (mean age = 20.98) at a university in Chongqing, China. The survey participants were 63.4% female and 36.6% male. The participants completed an online questionnaire which included Patient Health Questionnaire-9, Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7, Brief Barratt Impulsiveness Scale, Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support, and a 7-point scale to measure childhood SES. Descriptive statistics and correlation analyses were conducted for these variables, and the data examined further using a moderated conditional effect model with PROCESS macro (Model 8).
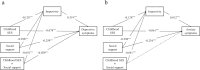
Results: The analysis revealed that lower childhood SES showed small to moderate negative correlations with impulsivity (r = -0.224, p < 0.01, small effect) and heightened symptoms of depression (β = -0.235, p < 0.01) and anxiety (β = -0.197, p < 0.01). Impulsivity shared variance with the link between childhood SES and both depressive (β = 0.386, SE = 0.011, p < 0.001) and anxiety symptoms (β = 0.315, SE = 0.012, p < 0.001). Higher levels of social support were linked to attenuated associations between low childhood SES and both impulsivity (β = -0.064, SE = 0.011, p < 0.01) and depressive symptoms (β = -0.029, SE = 0.010, p < 0.01). However, social support was not significantly associated with the link between childhood SES and anxiety symptoms.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that impulsivity serves as a partial intervening variable in the relationship between childhood SES and the mental health of first-year college students. However, higher levels of social support were linked to weaker negative associations between impulsivity and both childhood SES and mental health. Interventions that focus on managing impulsivity and increasing social support for first-year college students from low socioeconomic backgrounds could be effective strategies for improving their mental health.
Keywords: childhood socioeconomic status; first-year college students; impulsivity; mental health; social support.
Copyright © 2025 Kong, Su, Wang, Tan, Ran, Xu, Wang, Hong, Zhang and Kuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Association ACH. American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment Iii: Undergraduate Student Reference Group Data Report Spring 2023. Silver Spring, MD: American College Health Association; (2023).
-
- Gerdes H, Mallinckrodt B. Emotional, social, and academic adjustment of college students: A longitudinal study of retention. J Couns Dev. (1994) 72:281–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1556-6676.1994.tb00935.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources