Enhancing melanoma therapy with hydrogel microneedles
- PMID: 40313257
- PMCID: PMC12043666
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1590534
Enhancing melanoma therapy with hydrogel microneedles
Abstract
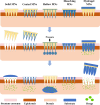
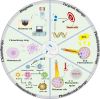
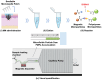
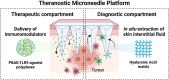
Melanoma is highly invasive and resistant to conventional treatments, accounting for nearly 75% of skin cancer-related deaths globally. Traditional therapies, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy, often exhibit limited efficacy and are associated with significant side effects due to systemic drug exposure. Microneedles (MNs), as an emerging drug delivery system, offer multiple advantages, including safety, painlessness, minimal invasiveness, and controlled drug release. Among these, hydrogel microneedles (HMNs) stand out due to their extracellular matrix-like structure and swelling-induced continuous hydrogel channels, which enable the direct delivery of therapeutic agents into the tumor microenvironment (TME). This approach enhances drug bioavailability while reducing systemic toxicity, establishing HMNs as a promising platform for melanoma treatment. This review highlights recent advancements in HMNs for melanoma therapy, focusing on their applications in biomarker extraction for early diagnosis and their role in supporting multimodal treatment strategies, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, phototherapy, targeted therapy, and combination therapy. Furthermore, the current matrix materials and fabrication techniques for HMNs are discussed. Finally, the limitations of HMNs in melanoma treatment are critically analyzed, and recommendations for future research and development are provided.
Keywords: cancer therapy; controlled release; drug delivery systems; hydrogel microneedles; melanoma.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Qiao, Gao, Jiang, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

