This is a preprint.
Development and clinical validation of blood-based multibiomarker models for the evaluation of brain amyloid pathology
- PMID: 40313266
- PMCID: PMC12045422
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.02.27.25322892
Development and clinical validation of blood-based multibiomarker models for the evaluation of brain amyloid pathology
Update in
-
Development and Clinical Validation of Blood-Based Multibiomarker Models for the Evaluation of Brain Amyloid Pathology.Neurol Clin Pract. 2025 Dec;15(6):e200546. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200546. Epub 2025 Oct 6. Neurol Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 41070139 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Plasma biomarkers provide new tools to evaluate patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) for Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. Such tools are needed for anti-amyloid therapies that require efficient and accurate diagnostic evaluation to identify potential treatment candidates. This study sought to develop and evaluate the clinical performance of a multi-marker combination of plasma beta-amyloid 42/40 (Aβ42/40), ptau-217, and APOE genotype to predict amyloid PET positivity in a diverse cohort of patients at a memory clinic and evaluate >4,000 results from "real-world" specimens submitted for high-throughput clinical testing.
Methods: Study participants were from the 1Florida AD Research Center (ADRC). Demographics, clinical evaluations, and amyloid PET scan data were provided with plasma specimens for model development for the intended-use cohort (MCI/AD: n=215). Aβ42/40 and ApoE4 proteotype (reflecting high-risk APOE 4 alleles) were measured by mass spectrometry and ptau-217 by immunoassay. A likelihood score model was determined for each biomarker separately and in combination. Model performance was optimized using 2 cutpoints, 1 for high and 1 for low likelihood of PET positivity, to attain ≥90% specificity and sensitivity. These cutpoints were applied to categorize 4,326 real-world specimens and an expanded cohort stratified by cognitive status (normal cognition [NC], MCI, AD).
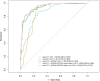
Results: For the intended-use cohort (46.0% prevalence of PET-positivity), a combination of Aβ42/40, ptau-217, and APOE4 allele count provided the best model with a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve (ROC-AUC) of 0.942 and with 2 cutpoints fixed at 91% sensitivity and 91% specificity yielding a high cutpoint with 88% positive predictive value (PPV) and 87% accuracy and a low cutpoint with 91% negative predictive value (NPV) and 85% accuracy. Incorporating APOE4 allele count also reduced the percentage of patients with indeterminate risk from 15% to 10%. The cutpoints categorized the real-world clinical specimens as having 42% high, 51% low, and 7% indeterminate likelihood for PET positivity and differentiated between NC, MCI, and AD dementia cognitive status in the expanded cohort.
Discussion: Combining plasma biomarkers Aβ42/40, ptau-217, and APOE4 allele count is a scalable approach for evaluating patients with MCI for suspected AD pathology.
Figures


References
-
- van Dyck CH, Sabbagh M, Cohen S. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Reply. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:1631–1632. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
