Rare paracholedochal lymph node metastasis in lung cancer
- PMID: 40313372
- PMCID: PMC12041744
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjaf260
Rare paracholedochal lymph node metastasis in lung cancer
Abstract
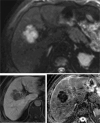
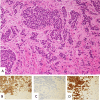
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Common metastatic sites include the liver, bones and adrenal glands, while intra-abdominal lymph node metastases (ALNM) are less frequently recognized and often underestimated. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of lung cancer cases. Gastrointestinal and intra-ALNM are rare but likely underdiagnosed, with hematogenous and lymphatic pathways, including the thoracic duct, playing key roles. ALNM occurs in 6%-11% of NSCLC patients, with the porta hepatis being an exceptionally rare site. Advanced staging and follow-up are crucial for detecting ALNM, as they impact prognosis and therapy. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) has shown superior sensitivity compared to CT in detecting extrathoracic metastases, influencing management in up to 25% of NSCLC cases. Here, we present the case of a NSCLC patient with a paracholedochal lymph node metastasis and explore various metastatic pathways emphasizing the pivotal role of PET/CT imaging.
Keywords: abdominal lymph node metastasis; choledochus; hepatoduodenal ligament; non-small cell lung cancer; staging PET/CT.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of JSCR Publishing Ltd 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

