Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in pediatric osteosarcoma with pulmonary metastases: a SEER database analysis
- PMID: 40313679
- PMCID: PMC12043881
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1574034
Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in pediatric osteosarcoma with pulmonary metastases: a SEER database analysis
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary metastasis (PM) is the most common site of distant metastasis in osteosarcoma (OS), particularly in pediatric cases, which are associated with poor prognosis. However, limited research has focused on identifying prognostic factors (PFs) for pediatric osteosarcoma with pulmonary metastasis (POPM). This study aims to identify clinical features and PFs of POPM and develop a validated nomogram to predict overall survival in POPM patients.
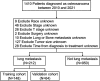
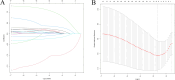
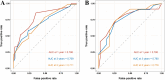
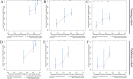
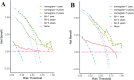
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using OS cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database (2010-2021). Clinical characteristics were compared between patients with and without PM. PFs were identified using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression and evaluated through Kaplan-Meier analysis. Patients were divided into training (N = 148) and validation (N = 64) cohorts. Independent PFs were determined via Cox regression to construct a prognostic nomogram, which was assessed using the concordance index (C-index), the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC), and calibration plots. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to evaluate clinical applicability.
Results: LASSO regression identified key PFs: AJCC stage, T stage, median household income, systemic therapy, and time from diagnosis to treatment. Among these, all except T stage were validated as independent PFs via Cox regression. The nomogram demonstrated strong predictive accuracy with C-index values of 0.68 (training) and 0.71 (validation). AUC values for 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival were 0.786, 0.709, and 0.711 in the training cohort and 0.780, 0.760, and 0.776 in the validation cohort. Calibration plots showed excellent concordance between predicted and actual survival, and DCA confirmed the nomogram's clinical relevance.
Conclusion: AJCC stage, median household income, systemic therapy, and time from diagnosis to treatment are significant PFs for POPM survival. The validated nomogram provides a valuable tool for personalized prognostic assessment and treatment decision-making in clinical practice.
Keywords: nomogram; osteosarcoma; pediatric osteosarcoma; prognosis; pulmonary metastasis.
© 2025 Tang, Guo, Lu, Fang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

