Cost-effectiveness analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis at low risk of surgical mortality in Sweden
- PMID: 40313688
- PMCID: PMC12045074
- DOI: 10.48101/ujms.v130.10741
Cost-effectiveness analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis at low risk of surgical mortality in Sweden
Abstract
Background: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has shown similar or improved clinical outcomes compared with surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis at low risk for surgical mortality. This cost-utility analysis compared TAVI with SAPIEN 3 versus SAVR in symptomatic severe aortic stenosis patients at low risk of surgical mortality from the perspective of the Swedish healthcare system.
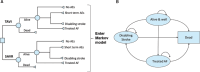
Methods: A published, two-stage, Markov-based cost-utility model that captured clinical outcomes from the Swedish Web-system for Enhancement and Development of Evidence-based care in Heart disease Evaluated according to Recommended Therapies (SWEDEHEART) registry (2018-2020) was adapted from the perspective of the Swedish healthcare system using local general population mortality, utility and costs data. The model had a lifetime horizon. Model outputs included changes in direct healthcare costs and health-related quality of life from using TAVI as compared with SAVR.
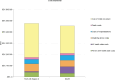
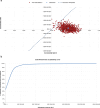
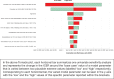
Results: TAVI with SAPIEN 3 resulted in lifetime costs per patient of 484,142 SEK Swedish krona (SEK) and lifetime quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) per patient of 7.16, whilst SAVR resulted in lifetime costs and QALYs per patient of 457,625 SEK and 6.81 QALYs, respectively. Compared with SAVR, TAVI offered an incremental improvement of +0.35 QALY per patient at an increased cost of +26,517 SEK per patient over a lifetime horizon, resulting in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of 76,532 SEK per QALY gained.
Conclusion: TAVI with SAPIEN 3 is a cost-effective option versus SAVR for patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis at low risk for surgical mortality treated in the Swedish healthcare setting. These findings may inform policy decisions in Sweden for the management of this patient group.
Keywords: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation; aortic stenosis; cost-effectiveness; low risk; surgical aortic valve replacement.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Upsala Medical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
KN: No conflicts to report. SJ: Proctoring fees from Medtronic. OA: Speaker fees from Abbott, Medtronic and Meril. Proctoring fees from Abbott. JB: No conflicts to report. HB: Consultancy for Edwards Lifesciences and Boston Scientific. PC: Employee of Edwards Lifesciences. MG: Consulting honoraria for Boston Scientific and Medtronic. HH: No conflicts to report. NEN: No conflicts to report. CM: Consulting compensation from Edwards Lifesciences for the Sweden specific costs, utilities and mortality inputs used in the model. AS: Employee of Edwards Lifesciences. MS: Proctoring/advisory board for Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences and Anteris. TB: Compensation from Edwards Lifesciences for consulting on developing the model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis at low risk of surgical mortality in Sweden.Ups J Med Sci. 2024 Nov 7;129. doi: 10.48101/ujms.v129.10741. eCollection 2024. Ups J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39691778 Free PMC article.
-
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation with SAPIEN 3 versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis at low risk of surgical mortality: a cost-utility analysis for Switzerland.Swiss Med Wkly. 2024 Oct 24;154:3558. doi: 10.57187/s.3558. Swiss Med Wkly. 2024. PMID: 39509083
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in aortic stenosis patients at low- and intermediate-surgical risk in Japan.J Med Econ. 2024 Jan-Dec;27(1):697-707. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2024.2346397. Epub 2024 May 6. J Med Econ. 2024. Update in: J Med Econ. 2024 Jan-Dec;27(1):803-804. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2024.2360835. PMID: 38654415 Updated.
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients With Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis at Low Surgical Risk: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Nov 2;20(14):1-148. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 33240455 Free PMC article.
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients With Severe, Symptomatic Aortic Valve Stenosis at Intermediate Surgical Risk: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Mar 6;20(2):1-121. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 32194880 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
